-
松枯梢病(又名松梢枯病shoot blight of pine)是世界范围内针叶树种上分布最广、最常见的重要林木枝干病害之一[1]。自从我国自20世纪70年代末报道以来,松枯梢病已蔓延至黑龙江、吉林、辽宁、陕西、江苏、湖北、福建、安徽、江西、广东和广西等10余个省份[2],严重危害松属(Pinus)、冷杉属(Abies)、落叶松属(Larix)、崖柏属(Thuja)、雪松属(Cedrus)、刺柏属(Juniperus)、云杉属(Picea)和黄杉属(Pseudotsuga)约8属60多种针叶树种[3]。该病害病原存在基因型的分化,De Wet通过多基因系谱学和微卫星标记手段将松枯梢病原菌划分为3个不同类型,分别为A型Diplodia scrobiculata,B型Diplodia seriata和C型Sphaeropsis sapinea(同物异名:Diplodia pinea)[4]。在中国引起松枯梢病的病原菌是C型松球壳孢菌(Sphaeropsis sapinea)[5],该病原菌可危害大树和幼树,大树多为侧枝发病,小树上顶梢发病,导致顶芽枯死、枯梢、根腐,严重时会出现流脂现象[6],对松树人工林造成了严重危害。目前,对松枯梢病主要采取化学防治与营林措施相结合的防治技术[7]。但长期使用化学农药不仅会导致环境污染、农药残留、威胁人类健康,而且容易诱导病原菌产生抗药性[8],甚至会导致病害的再次流行。而营林措施见效慢,投入成本较大。为有效防控松枯梢病,必须寻求一种生态友好的防治策略,木霉菌由于特有的拮抗和促生作用,现已成为一类应用较多的生防真菌[9],它通过竞争、寄生或产生抗菌素等次生代谢产物,从而对病原菌起到抑制作用[10],并能促进植物生长[11],提高寄主抵抗性。常见的生防木霉有哈茨木霉(Trichoderma harzianum)、绿色木霉(T. viride)、棘孢木霉(T. asperellum)等。研究表明,哈茨木霉ES323可有效抑制番茄灰霉病菌灰葡萄孢菌菌丝生长,引起菌丝腔质液泡化并导致菌体裂解[12]。非洲哈茨木霉菌(Trichoderma afroharzianum)株NAIMCC-F-01938发酵液可使葡萄白粉病原菌分生孢子扭曲变形,可作为安全杀菌剂在田间使用,可使葡萄白粉病发病率降低43%[13]。接种棘孢木霉可使洋葱鳞茎内酚类化合物含量提高97.6%,提高了洋葱对叶枯病的抵御能力,对洋葱叶枯病病原菌Stemphylium vesicarium具有显著的防控效果[14]。内生木霉菌株V76-12可抑制油棕叶斑病原菌Curvularia oryzae菌丝生长,同时提高了油棕幼苗苯丙氨酸解氨酶PAL、过氧化物酶POD和多酚氧化酶PPO的活性[15],提高了寄主植物的抗性。在前期的研究中,本实验室以松枯梢病原松球壳孢菌(Sphaeropsis sapinea)为目标菌株,从土壤真菌中分离筛选到1株对松球壳孢菌具有良好抑菌效果的森吉木霉菌株M75。为明确森吉木霉M75对松球壳孢菌的抑制作用机理,本研究从森吉木霉M75对病原菌代谢系统酶活性和电导率、丙二醛含量等方面,探究生防菌森吉木霉M75发酵粗提液对松球壳孢菌的抑菌机制,为松枯梢病的生物防治提供理论依据。
-
松球壳孢菌(Sphaeropsis sapinea)由中国林业科学研究院森林保护重点实验室菌种保藏中心提供。森吉木霉M75由本实验室分离筛选获得,现保藏于中国林业微生物菌种保藏管理中心,保藏编号:CFCC54490。
-
将保藏的M75菌株接种于PDA培养基上,28℃活化5 d,用打孔器选取直径5 mm菌饼,接入装有250 mL PDB培养液的三角瓶中,180 r·min−1、28 ℃振荡培养4 d,10000 r·min−14℃离心10 min,取上清经0.45 μm无菌微孔滤膜过滤,得到发酵粗提液,于4 ℃冰箱中保存备用。
-
将保藏的松球壳孢菌菌株接种于PDA培养基上,28 ℃活化5 d,用打孔器选取直径5 mm菌饼,接入装有250 mLPDB培养液的三角瓶中,160 r·min−1、28 ℃振荡培养3~4 d,将产生的直径约为2 cm的病原菌菌丝团用无菌水洗净后置于20 mL含20%发酵粗提液的无菌水溶液中,静置2、4、6、8、10、12、24、48、72、96 h后测定松球壳孢菌各项代谢酶活性和生理指标。以不添加发酵粗提液作为空白对照,每个时间段处理重复3次,指标测定时技术重复3次。
-
测定的病原菌代谢系统酶包括:保护酶系统中的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、多酚氧化酶(PPO);糖酵解途径中的己糖激酶(HK)、丙酮酸激酶(PK)和乳酸脱氢酶(LDH);三羧酸循环中的琥珀酸脱氢酶(SDH)和苹果酸脱氢酶(MDH);辅酶Ⅰ含量和ATP酶。酶活性测定试剂盒由南京建成生物工程研究所提供。
生理指标包括电导率、丙二醛(MDA)含量2个指标。电导率测定使用电导仪测定[16],丙二醛含量测定采用硫代巴比妥酸法[17]。
-
采用Excel 2010软件对实验数据进行统计和分析,绘图使用Origin 2018软件。
-
如图1所示,经森吉木霉M75粗提液处理的前8 h内,与对照组相比,松球壳孢菌代谢系统SOD酶活性显著上升,并在处理8 h时达到峰值,此时酶活性为72.717 U·(g·min)−1。说明病原菌在粗提液的处理下,前期SOD酶活性增加以达到保护菌体的作用。处理8 h后,SOD酶活性大幅降低,在处理96 h时酶活性最低,为1.510 U·(g·min)−1,说明随着处理时间增加,SOD酶活性不断降低。对照组在前8 h内SOD酶活性也呈上升趋势,8 h时酶活性达37.167 U·(g·min)−1,显著低于同时段处理组酶活性。但8 h后,对照组SOD酶活性呈平稳变化趋势,无大幅下降,48 h时达峰值62.180U·(g·min)−1,在处理96 h时酶活性为52.985 U·(g·min)−1。

Figure 1. Effects of the crude extract of Trichoderma songyi M75 on pathogen protective enzyme activities
经森吉木霉M75粗提液处理的前12 h内,CAT酶活性快速上升并在12 h时达到峰值,0.067 U·(g·s)−1,说明发酵粗提液导致松球壳孢菌代谢系统中过氧化氢含量增加,但处理12 h后酶活性大幅下降,并逐渐趋于零,在处理96 h时为0.004 U·(g·s)−1,是由于SOD酶活性逐渐降低,及膜脂过氧化严重,导致CAT酶活性不断降低。而对照组在48 h内CAT酶活性都处于上升状态,在48 h时达到峰值0.064 U·(g·s)−1,在之后随时间增加酶活性缓慢下降,96 h时为0.054 U·(g·s)−1,且在24 h后对照组CAT酶活性始终高于处理组。
在经森吉木霉M75粗提液处理的前12 h内,与对照组相比,松球壳孢菌代谢系统POD酶活性显著上升,在12 h时达到峰值,为5.733 U·(g·s)−1,在12 h后,处理组酶活性大幅下降,并在48 h后趋于平稳。对照组POD酶活性一直呈上升趋势。PPO酶活性与POD酶活性变化趋势基本一致,处理组在10 h时达到酶活性峰值,11.909 U·(g·s)−1,此后酶活性大幅快速下降,并在处理96 h时达到最低值0.046 U·(g·s)−1。
-
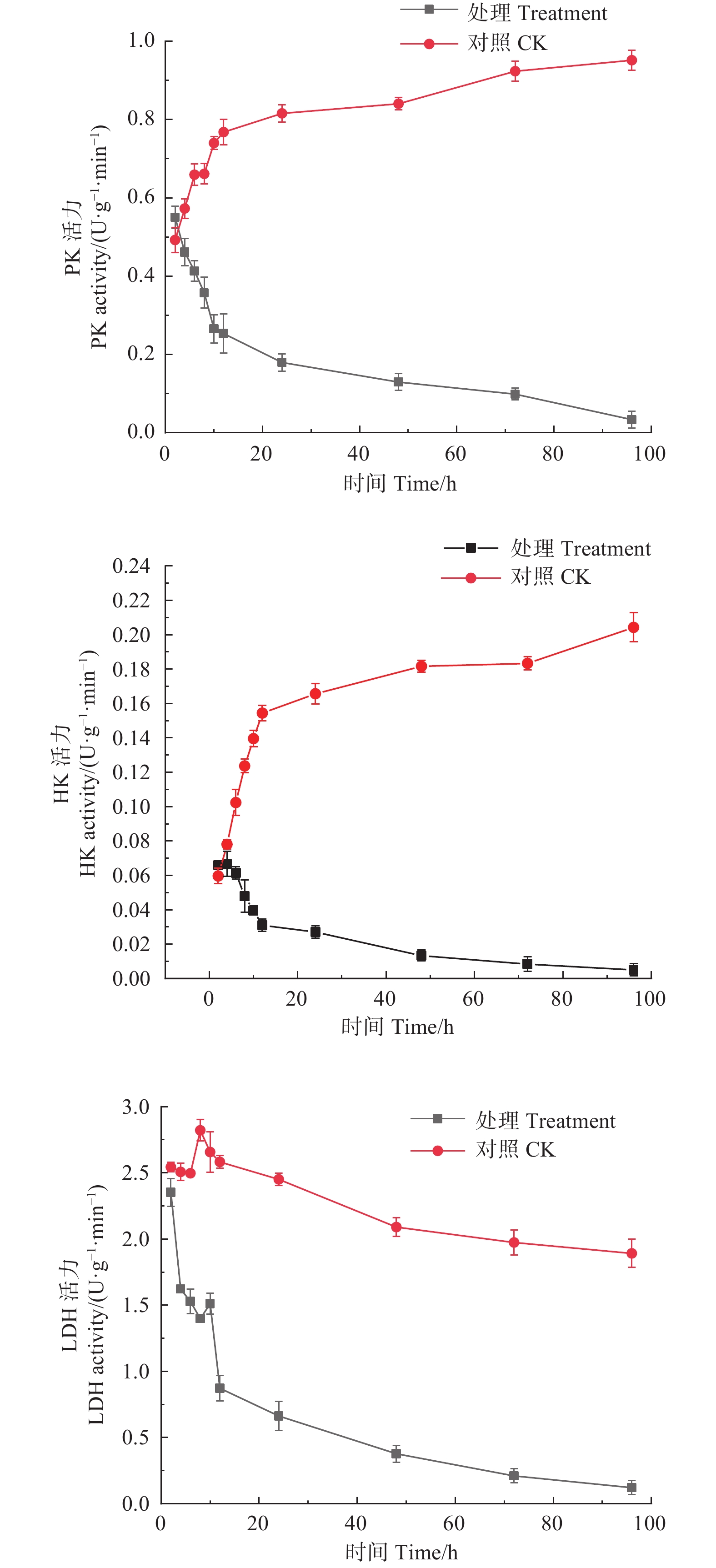
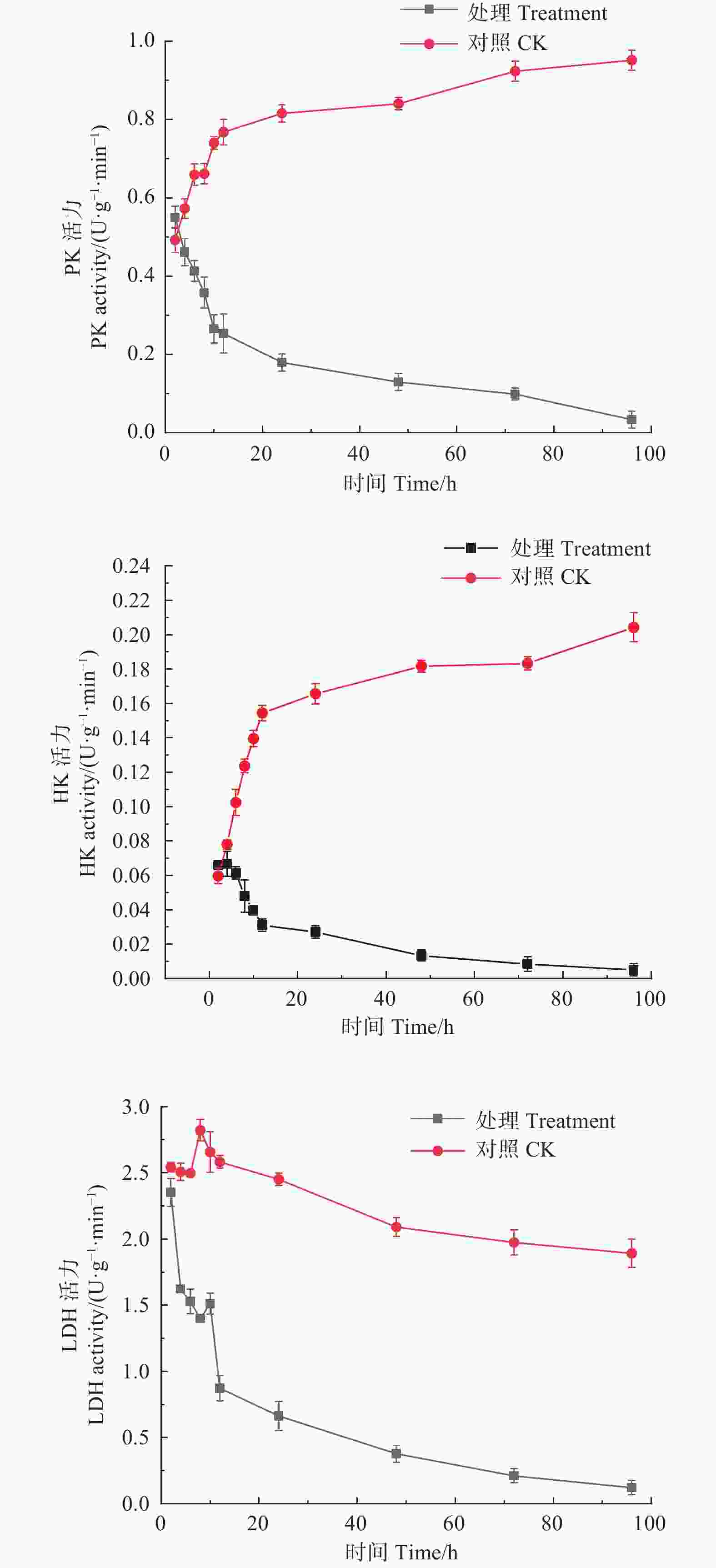
如图2所示,经M75发酵粗提液处理后,松枯梢病原菌松球壳孢菌菌丝团的PK、HK、LDH均随时间增加呈下降趋势,PK酶活性从初始2 h时的0.550 U·(g·min)−1,至96 h时下降至0.033 U·(g·min)−1。HK酶活性从初始2 h时的0.066 U·(g·min)−1,至96 h时下降至0.005 U·(g·min)−1。LDH酶活性由初始2 h的2.351 U·(g·min)−1,至96 h时下降至0.122 U·(g·min)−1。而对照组的PK、HK活力都随时间增加呈持续上升趋势,PK酶活性由初始2 h的0.492 U·(g·min)−1,至96 h时上升至0.952 U·(g·min)−1;HK酶活性由初始2 h的0.060 U·(g·min)−1,至96 h时上升至0.204 U·(g·min)−1;对照组的LDH酶活性整体趋于平稳,且酶活性始终高于处理组,说明M75发酵粗提液对糖酵解途径中的PK、HK及LDH的合成产生了抑制作用,严重干扰了其正常代谢。
-
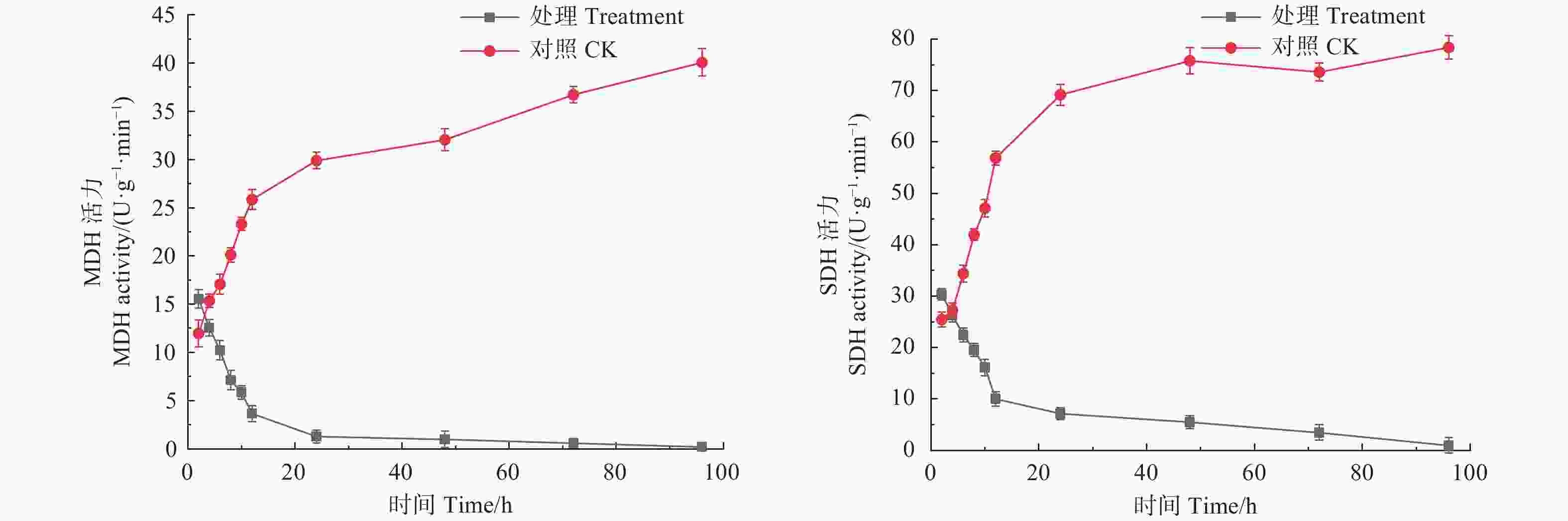
琥珀酸脱氢酶SDH是细胞能量代谢的重要酶类,其活性变化可直接反应细胞能量代谢状况[18]。如图3所示,经生防菌M75粗提液处理后,松球壳孢菌菌丝团的MDH与SDH酶活性在处理后的12 h内急速下降,MDH酶活性由初始2 h时的15.550 U·(g·min)−1下降至24 h时的1.275 U·(g·min)−1,之后下降趋势变缓,但仍随时间呈逐渐下降趋势,在96 h时为0.196 U·(g·min)−1。SDH酶活性在处理12 h内由初始2 h的30.327 U·(g·min)−1急速下降至9.997 U·(g·min)−1,之后下降趋势减缓,处理96 h时为0.948 U·(g·min)−1。而对照组MDH与LDH酶活性则随时间呈逐渐上升趋势。这说明粗提液抑制了病原菌代谢系统中MDH和SDH的正常合成,导致三羧酸循环停滞。
-
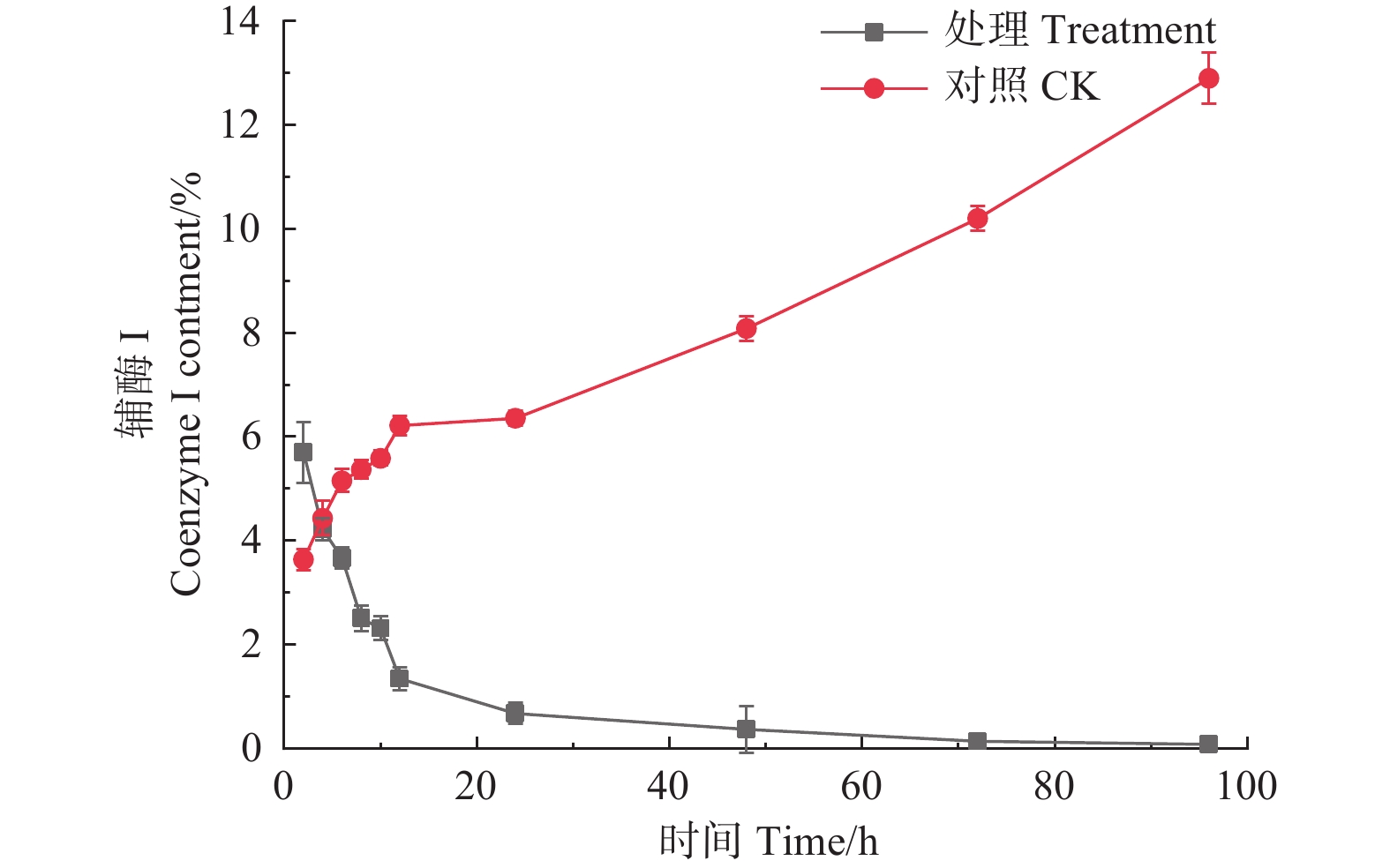
如图4所示,经森吉木霉菌M75发酵粗提液处理后的12 h内,松枯梢病原菌松球壳孢菌菌丝团的辅酶I含量快速下降,由2 h的5.700%下降至1.340%,在之后随处理时间的增加不断趋于零。对照组辅酶I含量则不断增加。
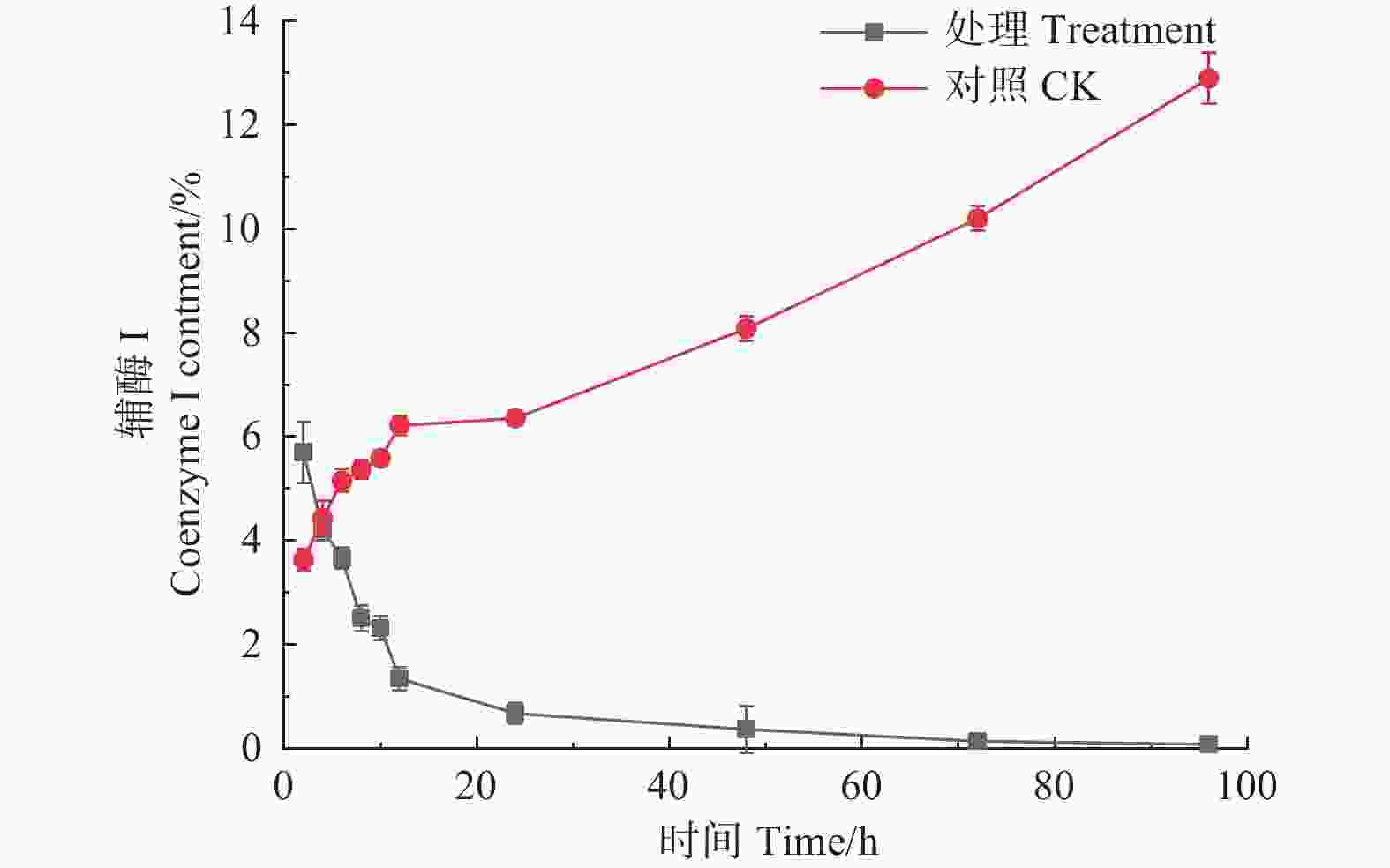
Figure 4. Effects of the crude extract of Trichoderma songyi M75 on the content of pathogens enzyme I
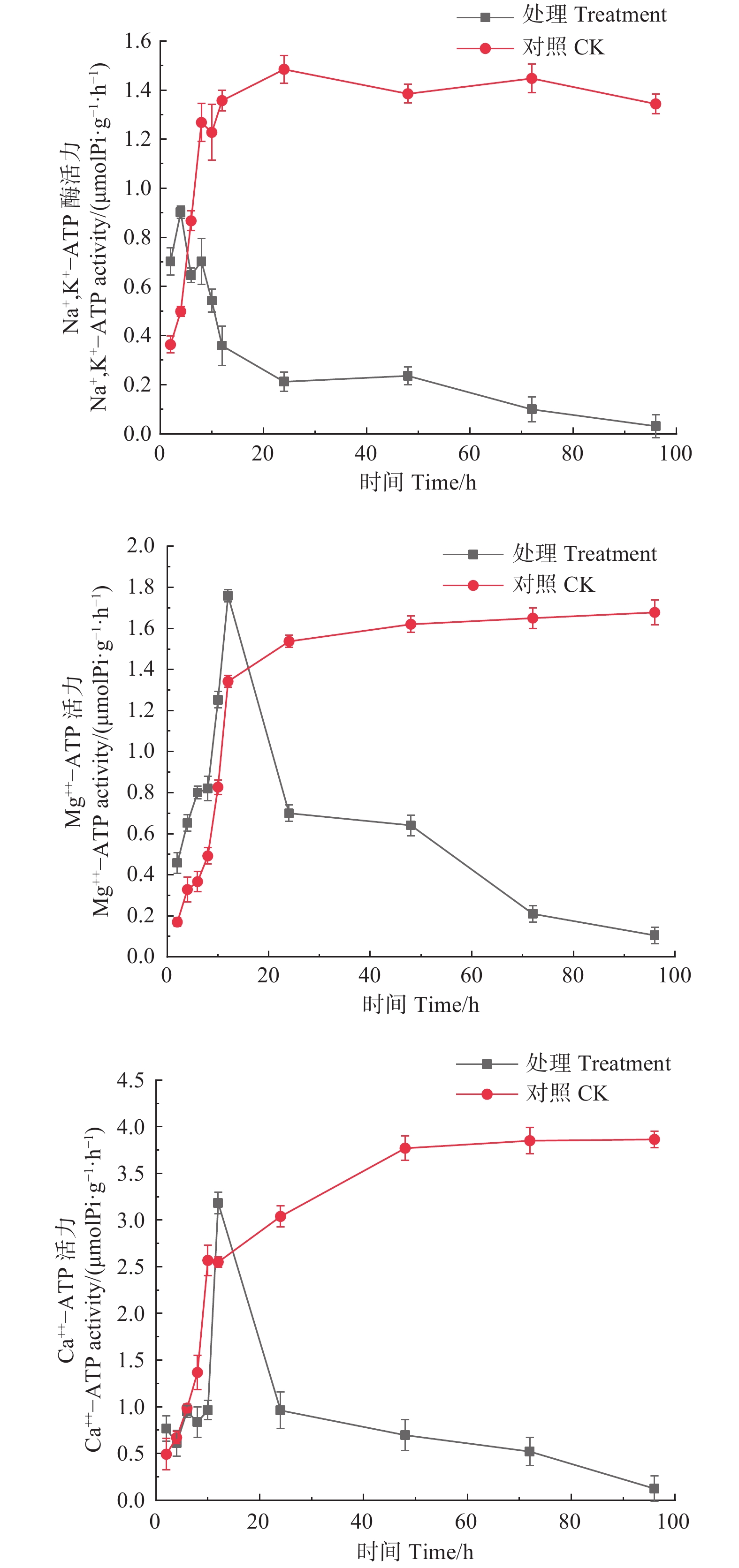
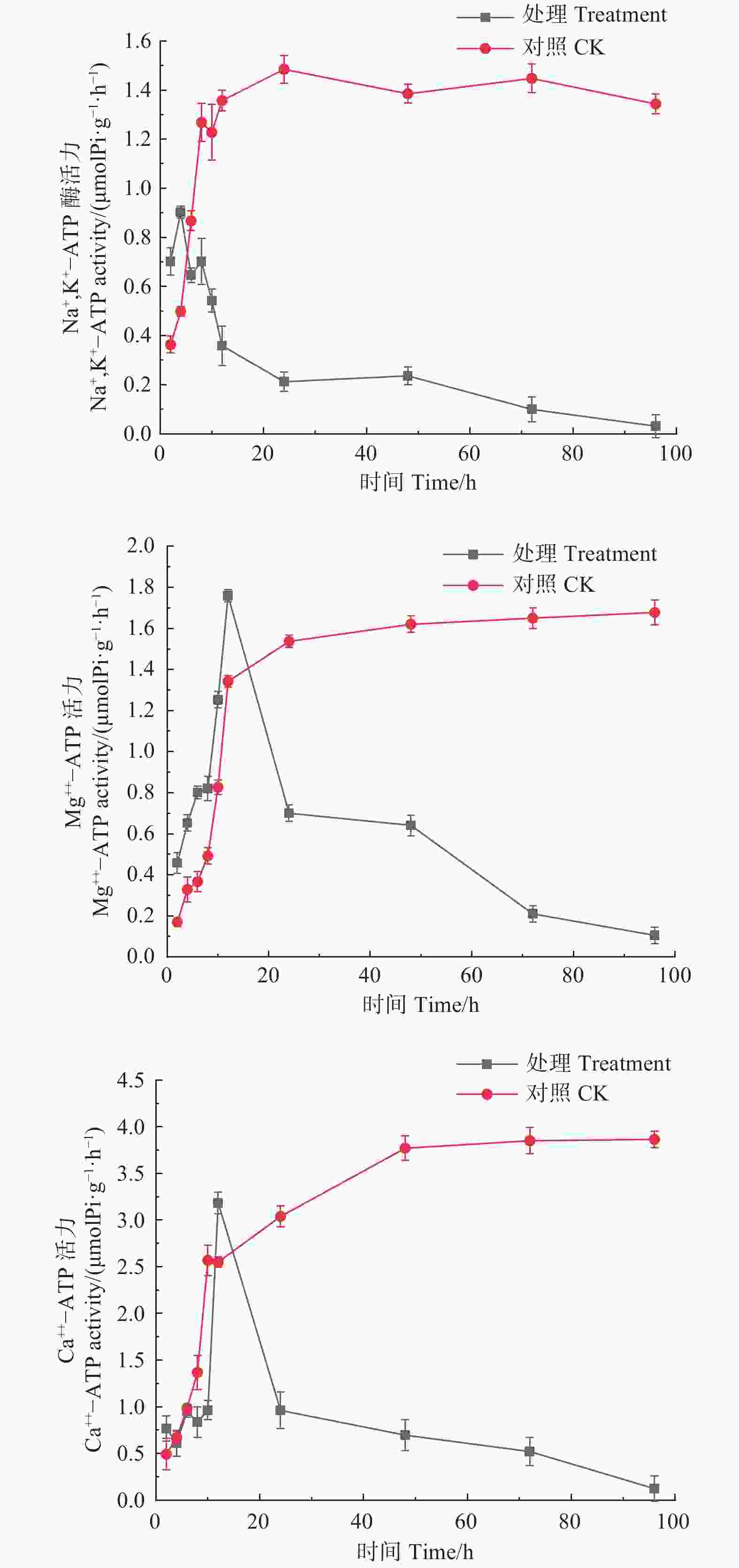
如图5所示,经森吉木霉菌M75发酵粗提液处理的Na+,K+-ATP、Mg2+-ATP、Ca2+-ATP酶活性总体上呈先上升后急速下降的趋势。处理4 h时,Na+,K+-ATP酶活性达到峰值0.902 μmol Pi·(g·h)−1,处理12 h时,Mg2+-ATP、Ca2+-ATP酶活性达到峰值,分别为1.759和3.184 μmol Pi·(g·h)−1,此后急剧下降并逐渐趋于零。对照组酶活性在24 h内处于快速上升趋势,后上升趋缓,但酶活性在10或12 h后高于处理组。
-
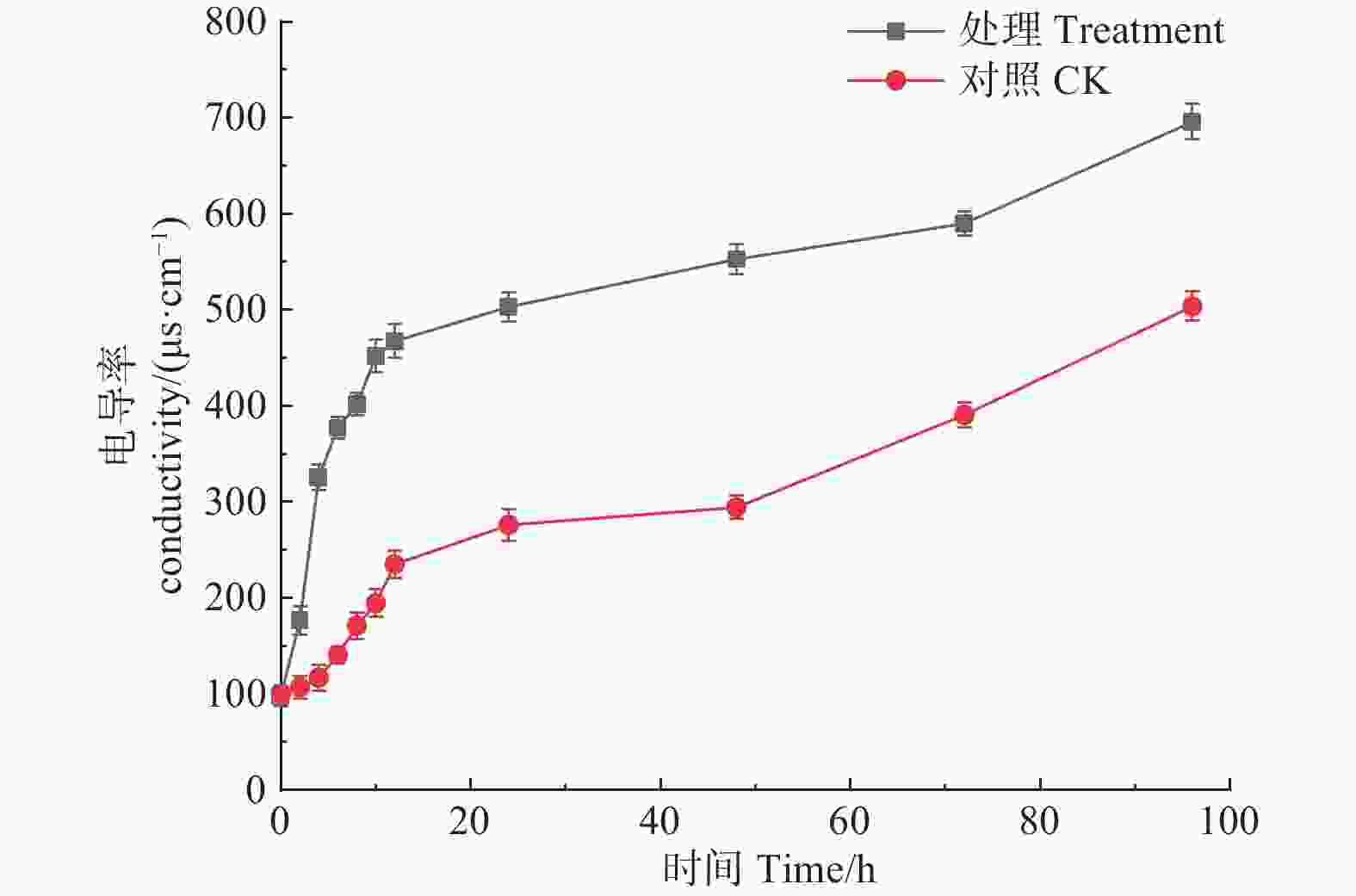
如图6所示,松球壳孢菌经森吉木菌M75发酵粗提液处理后,电导率随处理时间呈明显增大趋势,并且在各处理时段都远高于对照组,说明经处理的病原菌体电解质泄露,导致电导率值增加。
-
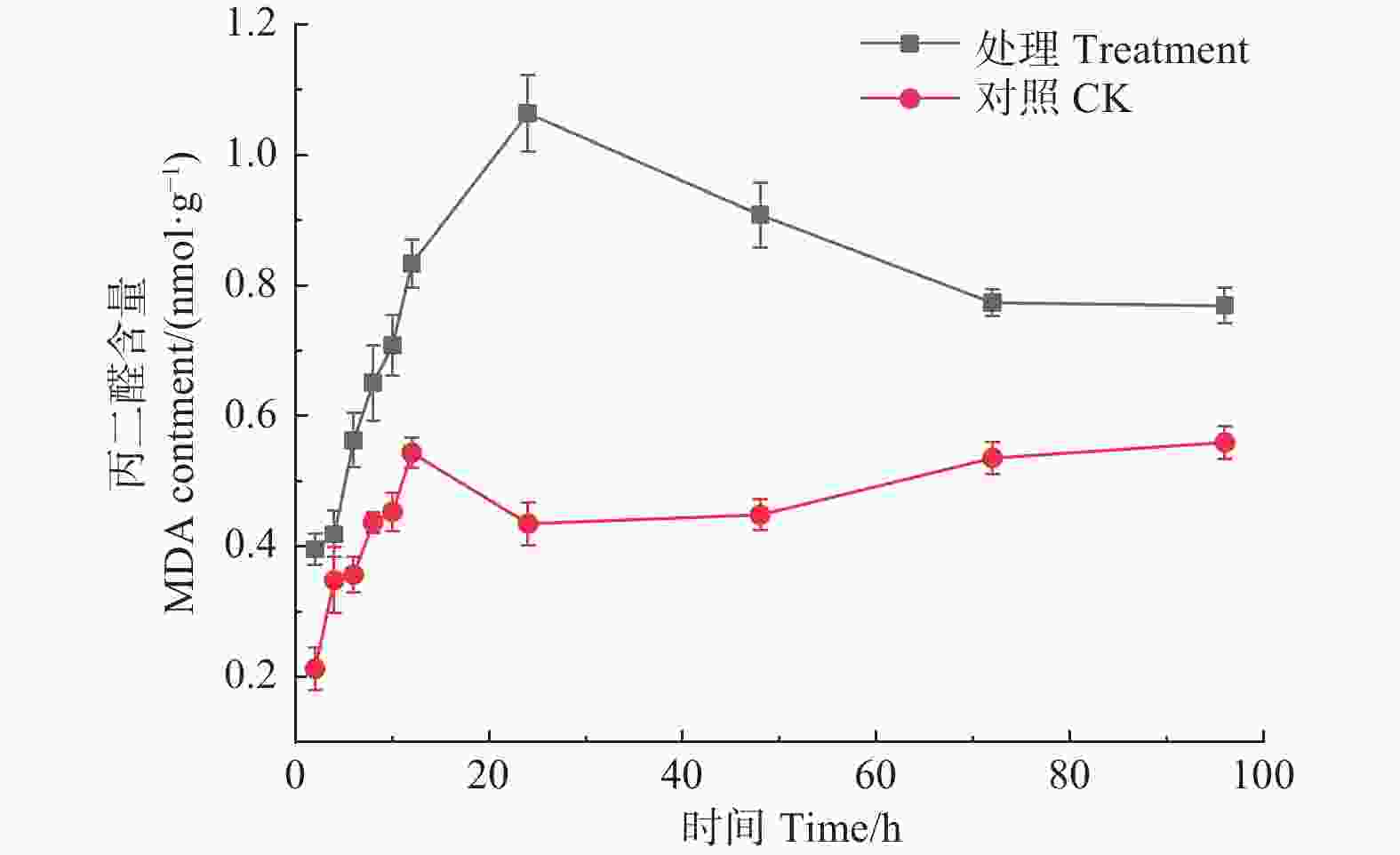
如图7所示,经森吉木霉M75粗提液处理后,松球壳孢菌MDA含量在24 h内呈急速增加趋势,在24 h时达到峰值,1.063 nmol·g−1,而后呈下降趋势。对照组MDA含量整体随时间增加呈平稳上升趋势,且对照组MDA含量始终低于处理组。
-
木霉菌作为应用最广泛的一类生防真菌,对18个属的29种植物病原真菌表现出显著的抑菌活性[19],生防菌株能够抑制病原菌的生长,必然是破坏了菌体正常的生理代谢途径[20]。森吉木霉M75发酵粗提液对松枯梢病原菌松球壳孢菌的抑制作用主要体现在,发酵粗提液有效抑菌成分可使松球壳孢菌代谢保护酶系统中的SOD、CAT、POD、PPO酶活性先上升后下降,并在处理10 h至12 h后显著低于正常水平,说明随着处理时间增加,氧自由基不断增多,细胞膜脂过氧化加重,导致保护系统酶活性不断降低,影响了病原菌保护酶系统的正常代谢。同时导致糖酵解途径中的HK、PK和LDH酶活性持续下降,影响了松球壳孢菌正常的糖酵解途径[21]。作为三羧酸循环中的关键酶,SDH和MDH代表TCA循环活化状态[22],其酶活数值变化能直接反应细胞能量代谢的情况[23],SDH与MDH活性降低,代表菌体的TCA循环受阻,正常的细胞代谢无法进行。ATP是生命体维持生命活动的能量库,其含量能在一定程度上反应出自身的生理状态[24],辅酶I含量可用于评价糖酵解和TCA循环的强弱,ATP和辅酶I的变化曲线反映出菌体在受到发酵粗提液胁迫时,细胞代谢路径受阻,糖酵解和TCA循环合成减慢,细胞能量供给不足[25]。MDA是细胞膜脂过氧分解的主要产物,MDA的含量可直接反映细胞膜过氧化程度[26],当生物体受到胁迫时,会引起细胞质膜过氧化,使得MDA含量大幅上升[27],本研究中松球壳孢菌MDA含量在处理24 h内急剧上升,且处理组MDA含量始终高于对照组,说明发酵液导致病原菌菌体过氧化程度加剧[28]。细胞内物质成分渗出是菌体膜脂受损的标志,能直接反映菌体细胞膜通透性的变化[29],本研究中松球壳孢菌的电导率随处理时间增加,电导率值不断上升,说明发酵粗提液破坏了菌体细胞膜的完整性,使菌体细胞膜透性改变,导致电解质渗漏[30],抑制了松球壳孢菌的正常生长。本研究中所用为此前分离得到的森吉木霉M75,这是森吉木霉首次应用于生物防治,目前还未见有关森吉木霉菌抑菌机理的报道,本研究对丰富生防木霉菌的资源库具有重要意义。
-
通过对松枯梢病病原菌松球壳孢菌代谢系统中保护酶系统、糖代谢、三羧酸循环、能量代谢中各关键酶和电导率、MDA含量等指标的测定,说明森吉木霉M75发酵粗提液对松枯梢病原松球壳孢菌有较好的抑制作用,可使其代谢系统相关酶活性降低,并导致电解质外渗,电导率升高,MDA大量累积,阻碍松球壳孢菌正常的生理代谢途径,使得病原菌无法进行正常的生理生化反应,从而抑制病原菌的生长。
Study on the Inhibition Mechanism of Trichoderma songyi Against Sphaeropsis sapinea
- Received Date: 2021-04-25
- Accepted Date: 2021-06-22
- Available Online: 2021-12-20
Abstract:






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: