-
松材线虫(Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)引起的病害被称为松树的“癌症”,具有传播迅速、繁殖力强,致死树木快的特点,松树感染松材线虫病后最快40天就可死亡,松林感病后3~5年即可毁灭,松材线虫是目前我国最为严重的森林有害生物,对我国以林业为主的生态环境建设造成重大威胁[1]。截止至2020年,松材线虫病的疫区已达18省667个县(区)[2]。辽宁省于2018年被正式确定为松材线虫病新发生区,疫点涉及7市22县[2],这是我国首次在年均温度10℃以下的地区发现松材线虫病的危害[3]。松材线虫病的传入直接威胁到辽宁省大面积的松林,以及沈阳市东陵和北陵等世界自然文化遗产,各自然保护区和风景名胜区的重点生态区域的安全,严重影响社会和经济发展。
松材线虫虽然危害严重,但却不能自行传播扩散,必须借助松褐天牛(Monochamus alternatus)等媒介昆虫才能传播蔓延。根据前人的研究发现,能够传播松材线虫病的媒介昆虫种类集中在墨天牛属[4-16]。目前发现在我国能携带且能成功传播松材线虫的媒介昆虫有两种:松褐天牛和云杉花墨天牛(Monochamus saltuarius Gebler)[4-5]。其中,云杉花墨天牛为辽宁省中温带地区新发现的特有的松材线虫病媒介昆虫[4,6],主要危害辽宁地区的红松(Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.)、油松(Pinus tabuliformis Carr.)、日本黑松(Pinust hunbergii Parl.)、华山松(Pinus armandii Franch.)、樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Litv.)、长白落叶松(Larix olgensis Henry)、日本落叶松(Larix kaempferi (Lamb.) Carr.)和华北落叶松(Larix principis-rupprechtii (Mayr) Pilger)[6-9]。而在我国南方疫区主要媒介昆虫为松褐天牛,该天牛也是我国分布最广的松材线虫病媒介昆虫[5,10]。目前,关于辽宁松材线虫病发生区是否存在其他潜在媒介昆虫种类尚不明确,因此本研究对辽宁松材线虫病发生区携带松材线虫的天牛种类进行全面的调查和研究,旨在进一步明确辽宁松材线虫病发生区的传播媒介,这将对辽宁省防治松材线虫病有着至关重要的意义。
-
2018—2019年,选择辽宁省4个松材线虫病发生区,分别为抚顺、大连、本溪和丹东作为调查地点,并设立调查样地,样地具体的林分情况如表1所示。
地点
Location树种
Species林龄
Age/a树高
Height of tree/m胸径
DBH/cm冠幅
Crown/m树间距
Spacing of tree/m郁闭度
Crown density抚顺市大伙房实验林场
Dahuofang Forest
Farm of Fushun油松
Pinus tabuliformis Carr.50 ≥16 24~34 5~7 3~4 0.7 红松
Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.25~35 ≥11 18~22 4~6 3~4 0.7 大连市甘井子林区
Ganjingzi forest
region of Dalian黑松
Pinus thunbergii Parl.47 ≥16 24~28 5~8 3~5 0.7 丹东市凤城草河林场
Fengcheng Caohe Forest
Farm of Dandong红松
Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.30 ≥12 20 4~6 3~4 0.7 本溪市南芬县林场
Nanfen County Forest
Farm of Benxi红松
Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.20 ≥12 22 7~9 2~3 0.7 本溪本溪县林场
Benxi Forest Farm红松
Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.20~50 ≥13 20~28 5~7 4~5 0.7 Table 1. Stand condition of forest sample plots
-
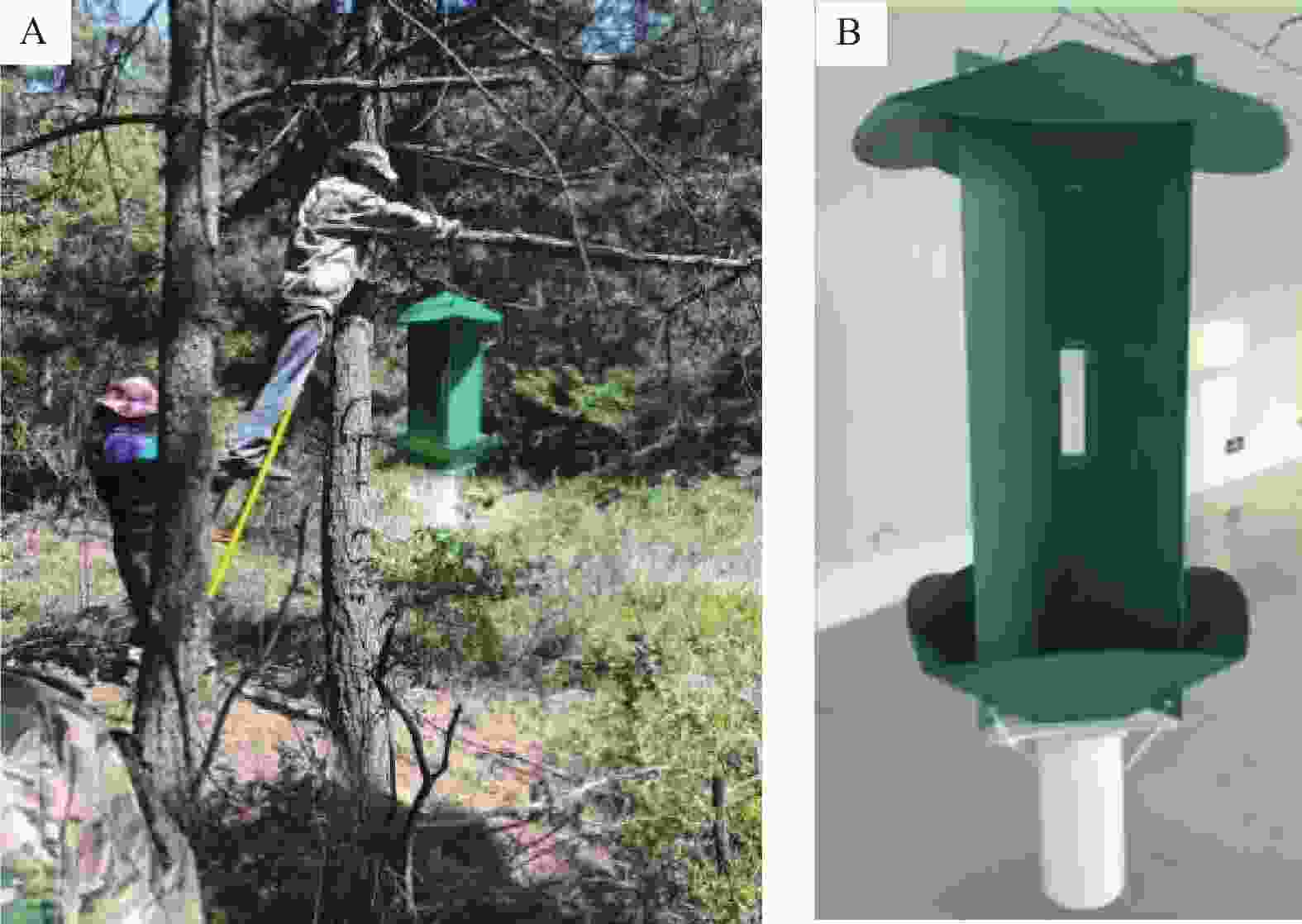
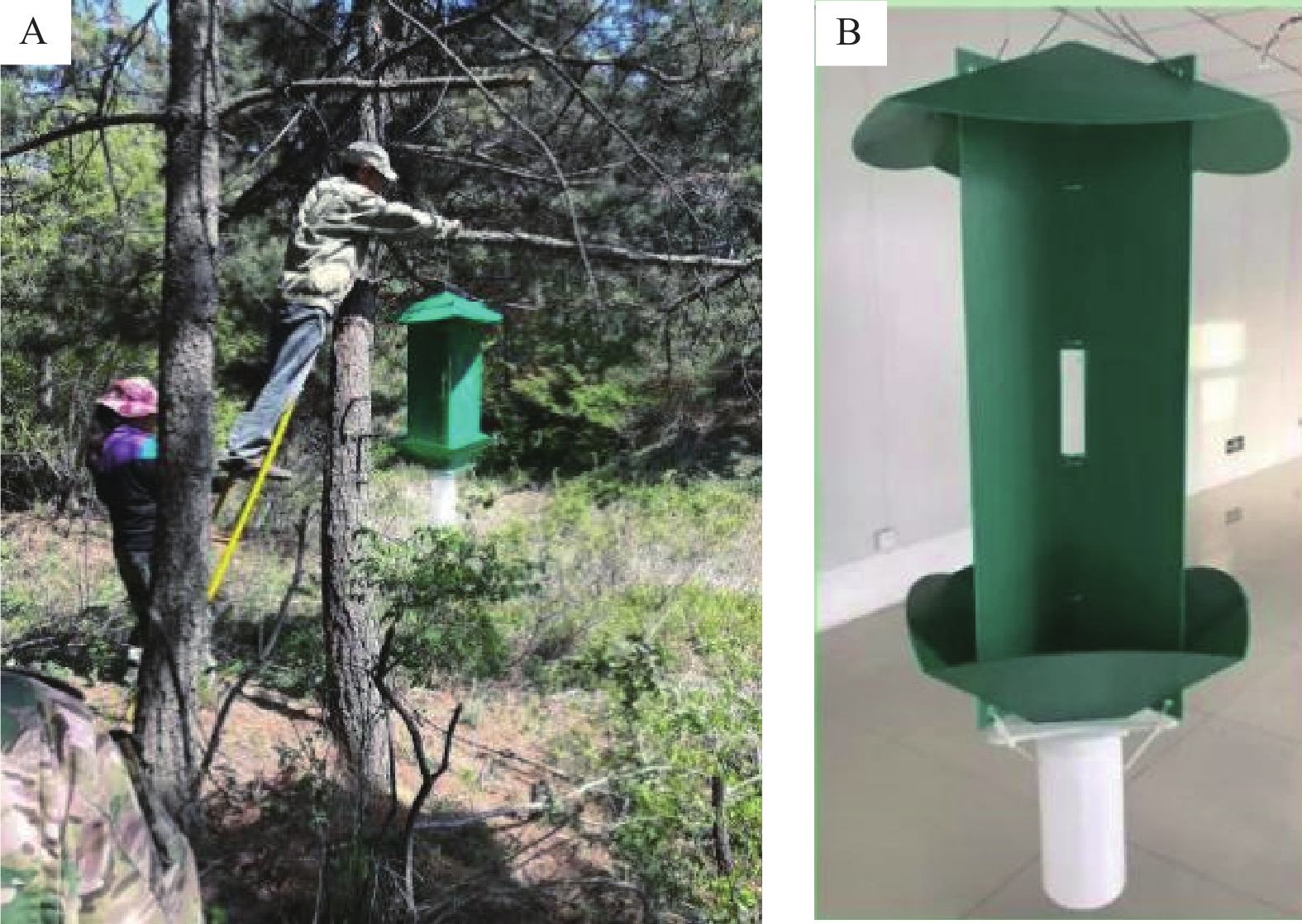
2018年至2019年,从5月上旬至9月下旬为天牛羽化期,在林地随机悬挂天牛诱捕器(ZM-80B型诱捕器和APF-I型媒介天牛高效诱芯),确保每块样地的林缘和林间均有悬挂诱捕器,悬挂间隔为50 m,悬挂高度1.5 ~2.0 m,每个月更换1次诱芯。每隔7 d收集诱捕到的天牛,并将诱捕到的天牛样品带回实验室,进行鉴定(图1)。
-
2020年4月,林地随机选取感染松材线虫病死亡且受天牛危害的疫木,将疫木锯成1 m长的木段,两端封蜡,用铁丝网幕(8目铁网)包裹,防止木段内的天牛逃逸。随后,将木段置于自然条件下,每天观察并及时收集新羽化的天牛,将收集到的天牛成虫带回实验室,统计数量(图2)。
-
参考《东北天牛志》[17]、《中国经济昆虫志:鞘翅目天牛科(一)》[10]、《中国经济昆虫志:鞘翅目天牛科(二)》[18]和《中国经济昆虫志:鞘翅目天牛科(三)》[19]等书籍以及其他文献资料,通过观察虫体各部分的形态学特征,如:体色、斑纹、体型、体长、鞘翅和头部等形态特征进行鉴定。
-
采用贝曼式漏斗法分离线虫[20],将从疫木中初羽化的云杉花墨天牛活体剪碎,包裹在四层纱布内,置于漏斗中并向漏斗内注入纯净水,确保虫体全部浸泡在水中。6 h后,将浸出液用1 000 r·min−1的转速离心5 min,弃上清液,查数浓缩液中线虫数量并备用。
-
(1)形态学鉴定。用100 μL移液枪挑取线虫浓缩液中的线虫成虫滴至载玻片上,将其置于酒精灯火焰上方加热3~5 s。线虫热杀后呈“J”形,加盖玻片,制成临时玻片,在显微镜下观察并鉴定线虫形态特征。参考《植物病原线虫学》[21]和来燕学方法[22],通过在解剖镜下观察松材线虫的体长、头部、中食道球,性器官,雌虫尾尖突等形态特征进行鉴定。
(2)基因组学鉴定。线虫DNA提取参考于海英[7]的方法,按照松材线虫检测试剂盒(南京生兴有害生物防治技术股份有限公司)要求的步骤提取线虫 DNA,进行实时荧光定量PCR扩增和检测。正向引物序列为正向引物序列为5′-GAGCAGAAACGCCGACTT-3′,反向引物序列为 5′-CGTAAAACAGATGGTGCCTA-3′,TaqMan探针序列为5′-TGCACGTTGTGACAGTCGT-3′,探针5′端标记发光基团为6-carboxyfluorescein(FAM),3′端标记的淬灭基团为tetramethyl-carboxy-rhodamine(TAMRA)将混合后的溶液放入松材线虫自动化分子检测仪(南京生兴有害生物防治技术股份有限公司)自动检测程序。即95 ℃ 运行10 min,循环程序: 95 ℃下运行15 s,60 ℃下运行35 s,共35个循环。
-
调查所得数据均利用Excel软件(Microsoft office 2020)进行整理,利用SPSS 23.0软件进行数据分析,相同样品不同处理间的比较采用单因素方差分析(SNK多重比较法,P≤0.05)。
-
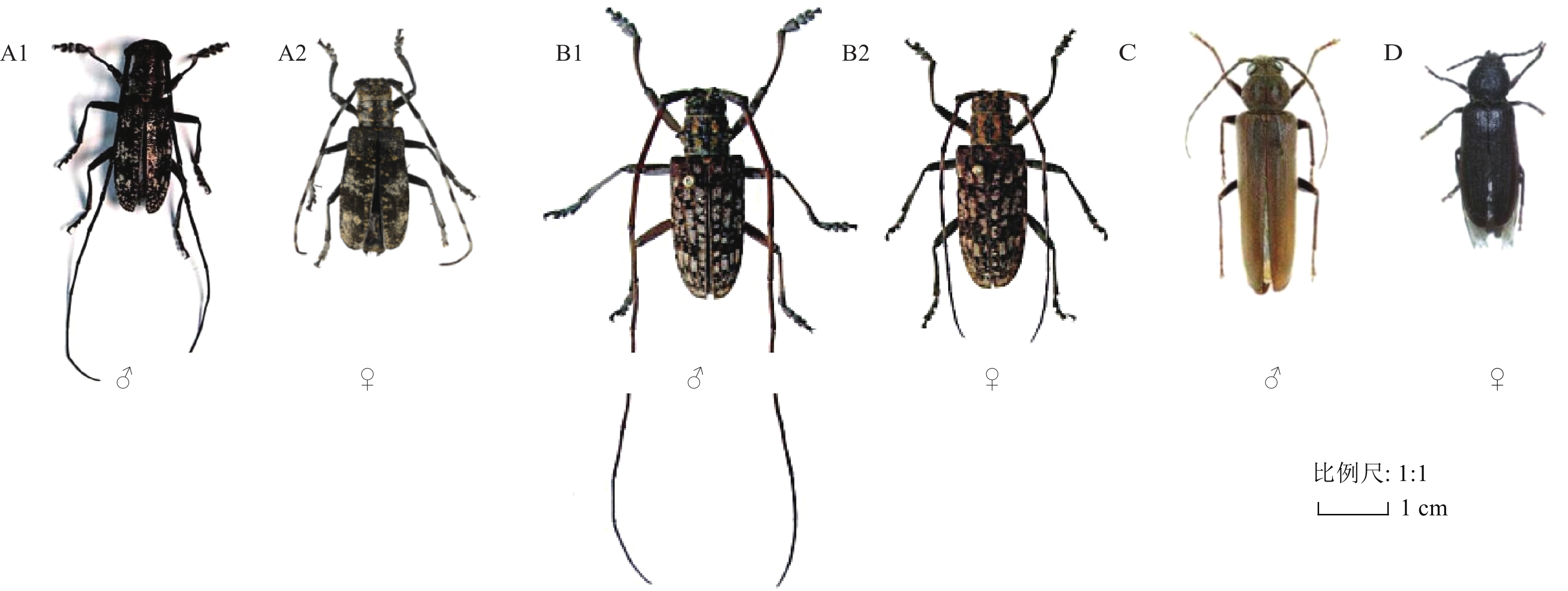
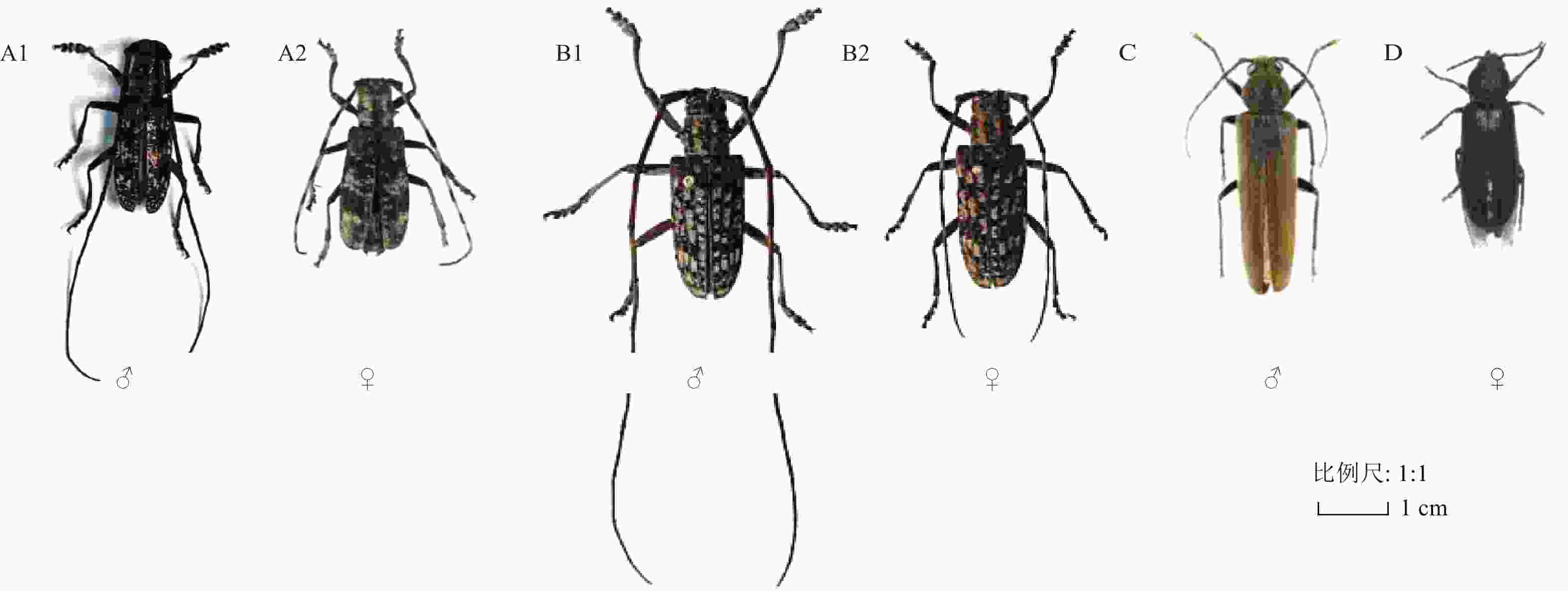
调查结果显示,在辽宁松材线虫病发生区共调查到9种天牛,分别是云杉花墨天牛、松褐天牛、褐梗天牛(Arhopalus rusticus)、脊鞘幽天牛(Asemum striatum)、松皮花天牛(Rhagium inquisitor)、小灰长角天牛(Acanthocinus griseus)、双簇污天牛(Moechotypa diphysis)、灰长角天牛(Acanthocinus aedilis)和钩突土天牛(Dorysthenes sternalis)。其中云杉花墨天牛的诱捕数量最多,为2 387头;其次依次是松褐天牛329头、褐梗天牛317头、脊鞘幽天牛84头、钩突土天牛41头、小灰长角天牛22头、松皮花天牛12头、灰长角天牛5头、双簇污天牛1头,通过查阅《东北天牛志》并根据林间实际情况,得出9种天牛的寄主植物(表2)。
序号
No.种名
Species调查地点
Survey location寄主松树
Host pine是否携带松材线虫
Is there any B. xylophilus诱捕数量
Number of traps1 云杉花墨天牛
Monochamus saltuariusA,B,C,D 油松,红松
Pinus tabuliformis Carr.,Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.√ 2387 2 松褐天牛
Monochamus alternatusE 黑松
Pinus thunbergii Parl.√ 329 3 褐梗天牛
Arhopalus rusticusA,B,C,D,E 油松,红松
Pinus tabuliformis Carr.,Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.√ 317 4 脊鞘幽天牛
Asemum striatumA,B,C,D 油松
Pinus tabuliformis Carr.√ 84 5 松皮花天牛
Rhagium inquisitorA,B 油松,红松
Pinus tabuliformis Carr.,Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.— 12 6 小灰长角天牛
Acanthocinus griseusA,C 红松
Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.— 22 7 双簇污天牛
Moechotypa diphysisA 油松
Pinus tabuliformis Carr.— 1 8 灰长角天牛
Acanthocinus aedilisA,B 油松,红松
Pinus tabuliformis Carr.,Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc.— 5 9 钩突土天牛
Dorysthenes sternalisA,B 云南松
(阔叶寄主树种:杨属,柳属,榆属)
Pinus yunnanensis Franch.
(Host broadleaved species: Populus, Salix, Ulmus)— 41 ①A: 抚顺市大伙房实验林场(Dahuofang Forest Farm of Fushun),B:丹东市凤城草河林场(Fengcheng Caohe Forest Farm of Dandong),C:本溪市南芬县林场(Nanfen County Forest Farm of Benxi),D:本溪市本溪县林场(Benxi Forest Farm),E:大连市甘井子林区(Ganjingzi forest region of Dalian) Table 2. The species and quantity of long-horned beetles of epidemic area in Liaoning
-
结合各个松材线虫病发生区具体情况,在辽宁省不同的松材线虫病发生区携带松材线虫的天牛种类存在差异(图3)。在抚顺、丹东和本溪疫区发现体内携带松材线虫的天牛共3种,分别是云杉花墨天牛、褐梗天牛和脊鞘幽天牛;在大连疫区发现体内携带松材线虫的天牛共3种,分别为松褐天牛、褐梗天牛和脊鞘幽天牛,4种天牛成虫形态见图4。其中,松褐天牛为大连疫区特有的体内携带松材线虫的天牛;云杉花墨天牛为辽宁省其他疫区特有的体内携带松材线虫的天牛。
-
在抚顺、丹东和本溪发生区,云杉花墨天牛成虫的诱捕数量均高于其他两种天牛的数量,该天牛的诱捕数量占相同疫区内的松树天牛诱捕总量的51%以上,为这几个地区的松林内数量最多的天牛种群;在大连疫区,褐梗天牛的诱捕数量较高,占天牛诱捕总量的62.43%,为松林内数量最多的天牛种群(图5)。
-
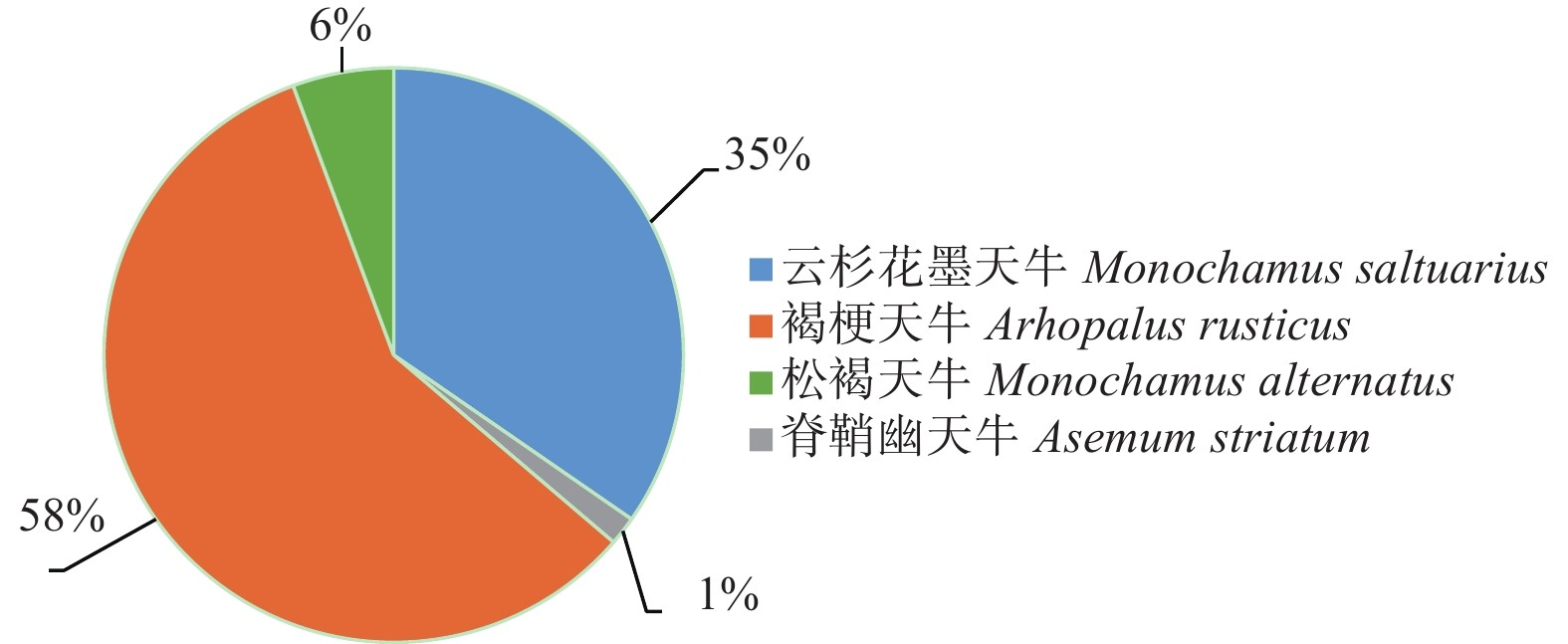
对诱捕器内收集到的松树天牛进行检测共发现4种124头天牛能携带松材线虫,其中褐梗天牛占比最大,为58%,其次依次是云杉花墨天牛35%,松褐天牛6%,脊鞘幽天牛1%(图6)。虽然褐梗天牛,脊鞘幽天牛能携带松材线虫,但其是否为媒介昆虫尚未有定论,参考于海英研究确定辽宁省松材线虫病的主要媒介昆虫为云杉花墨天牛,大连市疫区主要媒介昆虫为松褐天牛[4]。
通过疫木包网调查发现云杉花墨天牛成虫体内携带松材线虫的平均数量为513.69条·头−1,其中雌成虫体内携带松材线虫的平均数量为775.44条·头−1,最大值为10060 条·头−1,最小值为1 条·头−1;雄成虫体内携带松材线虫的平均数量为191.54 条·头−1,最大值为3620 条·头−1,最小值为1 条/·头−1(表3)。
成虫
Adult体内线虫数量
最大值/条
Maximum number
of nematodes体内线虫数量
最小值/条
Minimum number
of nematodestodes平均
数量/条Average
numberumber雌 Female 10060.00 1.00 775.44 雄 Male 3620.00 1.00 191.54 总计 Total 10060.00 1.00 513.69 Table 3. Number of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus carried by newly emerged Monochamus saltuarius adults
-
不同地区、不同种类的媒介昆虫体内携带松材线虫的数量均存在一定差异。前人研究发现北美卡罗莱纳墨天牛(Monochamus carolinensis)体内携带松材线虫的平均携带量均能达到1.9万余条·头−1[14],松褐天牛体内携带松材线虫的平均携带量为1.8万条·头−1[12],日本云杉花墨天牛携带量为9 000条·头−1[13]。本研究调查结果显示在辽宁省松材线虫病发生区,媒介天牛云杉花墨天牛体内携带松材线虫的数量既少于南方疫区松褐天牛的携带量,也少于日本云杉花墨天牛的携带量,然而松材线虫数携带量较少却也能够感染并致死红松和油松,可能与树种的抗病性较弱有关。分析云杉花墨天牛携带线虫量较少可能由于与体型有关:与松褐天牛相比,云杉花墨天牛体型较小[17],推测其气管的容积也相对较小,气管是媒介天牛携带松材线虫的主要部位[23],可能是由于云杉花墨天牛气管容积有限,所以无法携带较多的松材线虫,有关该天牛气管结构与容积大小对松材线虫携带与传播的影响有待进一步研究。同时天牛体内线虫携带量也可能与松树体内线虫的数量与分布有关,红松为辽宁特有的松材线虫病寄主树种[4],也是近年来新发现的中温带地区松材线虫病自然感病树种,松材线虫在病死红松内的发生数量和分布情况尚不明确,这些因素也会影响云杉花墨天牛携带松材线虫的数量。松褐天牛在辽宁松材线虫病发生区只分布在大连地区,且数量较少,本研究调查了诱捕器收集到的松褐天牛体内携带线虫数量,因无法确认供试松褐天牛是否通过补充营养的途径释放松材线虫,故其体内松材线虫的携带量较少,需要进一步调查初羽化松褐天牛体内携带松材线虫数量。
此外,调查发现林间褐梗天牛携带松材线虫比例相对较大,但褐梗天牛是否能够传播松材线虫还未得到证实。为有效控制松材线虫病在在辽宁省的危害,防止其继续向北扩散,我们仍需对:1)辽宁省松材线虫病发生区内潜在媒介昆虫种类;2)媒介昆虫在不同寄主松树上的生活史和危害特点;3)媒介昆虫在辽宁松材线虫病发生区的生物学特征和携带松材线虫传播规律;4)我国中温带地区褐梗天牛能否传播松材线虫等问题展开研究。
-
辽宁省作为松材线虫病的新发生区,松材线虫的发生规律、寄主植物的种类和媒介昆虫的种类均与我国其他松材线虫病疫区存在较大的差异。通过在林间悬挂诱捕器、包网疫木发现,辽宁松材线虫病发生区共调查到9种松树天牛,分别为云杉花墨天牛、松褐天牛、褐梗天牛、脊鞘幽天牛、松皮花天牛、小灰长角天牛、双簇污天牛、灰长角天牛和钩突土天牛。其中云杉花墨天牛、松褐天牛、褐梗天牛和脊鞘幽天牛体内携带松材线虫;明确了云杉花墨天牛和松褐天牛为辽宁省松材线虫病疫区的主要媒介昆虫。通过对松树天牛体内松材线虫携带量的调查发现,云杉花墨天牛和松褐天牛体内携带松材线虫的数量较少,而其他天牛体内可携带大量的松材线虫,由此推测其他天牛有可能成为辽宁省松材线虫病疫区的潜在媒介。
Study on the Species of Long-horned Beetles Carrying Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Liaoning
- Received Date: 2021-04-29
- Accepted Date: 2021-05-18
- Available Online: 2021-12-20
Abstract:









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: