-
沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides L.)隶属胡颓子科沙棘属,落叶灌木或小乔木,雌雄异株,广泛分布于 2°~115° E、27°~68°50′ N的欧亚大陆地区[1]。沙棘生态适应性极强,具有耐寒、耐旱、耐瘠薄、耐盐碱等优良特性,是营造防风固沙和水土保持林的先锋树种[2]。另外,沙棘也是药食同源植物,其果实以及根、茎、叶等各器官中均含有丰富的生物活性物质和营养成分,被广泛应用于医药、食品、化妆品等轻化工行业[3]。我国是世界上沙棘资源最丰富的国家,占世界沙棘资源的93%,其中,中国沙棘亚种(Hippophae rhamnoides L. subsp. sinensis Rousi)分布面积最广、数量最多、生态经济利用程度最高[4],而山西省分布的沙棘资源又占到全国野生资源的60%,均为中国沙棘。沙棘种质资源的丰富性为沙棘育种奠定了良好的基础。
表型性状分析是研究植物遗传多样性最直观、最有效的手段。研究植物表型性状不仅能了解植物的基因型与环境互作的机理机制,还能从中挖掘出经济和生态价值较高的特异基因性状,对促进植物种质资源的创新、创制和高效利用具有重要的理论及实践意义[5]。已有专家学者利用表型变异对大别山山核桃(Carya dabieshanensis M. C. Liu et Z. J. Li)[6]、砂生槐(Sophora moorcroftiana (Benth.) Baker)[7]、格木(Erythrophleum fordii Oliv.)[8]、尾叶樱桃(Cerasus dielsiana (Schneid.) Yu et Li)[9]、枫香树(Liquidambar formosana Hance)[10]、长柄扁桃(Amygdalus pedunculata Pall.)[11]、岷江柏(Cupressus chengiana)[12]等天然种群进行了多样性分析与评价,阐明了种群变异结构和来源,揭示了表型变异与地理生态因子之间的关系。
目前,我国沙棘良种选育工作主要集中在引种[13-16]、个体及群体遗传改良[17-21]等方面。也有学者对沙棘表型多样性进行研究,田广玉等[22]对陕西省黄龙县中国沙棘的性状变异与表型结构进行了研究;余天蓝等[23]对新疆6个天然居群野生沙棘果实性状多样性进行研究;黄铨等[24]对山西省关帝山中国沙棘种群表型结构进行研究,指出关帝山的中国沙棘是以主干型桔黄色、近圆果形植株为主体的多态型种群系统;吴琼等[25]选取了山西省境内7个和河北省1个中国沙棘天然种群对其表型多样性进行分析,发现山西省中国沙棘的表型性状有丰富多态性;陈汉鑫等[26]对山西省4个地区的45株沙棘单株进行结实性状和果实营养成分分析研究,筛选出在结实性状和果实品质上表现较优的优良单株。师瑞瑞等[27]对山西省方山县和青海省天峻县2个不同海拔的中国沙棘进行表型多样性研究,发现2个种群均具有丰富的表型多样性。然而,对山西省中国沙棘天然种群优树间的表型变异未见报道。本研究选取了山西省11个天然种群的中国沙棘优树,将不同种群的优良资源进行分析比较,旨在更系统、全面地揭示山西省不同中国沙棘种群优树间表型性状与生态因子的关系及其变异规律,为沙棘优良种质资源的收集、保存及遗传改良提供技术支撑。
HTML
-
2019年9月至 11月,完成中国沙棘选优、采样工作,共计11个种群,110个优良单株。每个种群内取样植株间距在50 m以上。各取样地点的基本情况见表1。
种群
Populations纬度
Latitude(N)经度
Longitude(E)海拔
Altitude/m年平均降水量
Precipitation/mm样本数
No. of individual右玉 Youyu 40°5′~40°13′ 112°24′~112°33′ 1346~1843 406.9 8 云州 Yunzhou 39°59′~40°10′ 113°33′~113°46′ 943~1315 369.3 10 广灵 Guangling 39°49′ 113°54′~113°55′ 1923~2098 372.2 14 五寨 Wuzhai 38°54′~38°55′ 111°53′~111°54′ 1774~1867 460.6 6 原平 Yuanping 38°49′~38°56′ 112°21′~112°25′ 1507~1809 411.9 4 宁武 Ningwu 38°49′~38°55′ 112°8′~112°23′ 1609~1638 427.4 4 岢岚 Kelan 38°43′~38°47′ 111°43′~111°46′ 1537~1980 444.6 6 兴县 Xingxian 38°17′~38°26′ 111°24′~111°34′ 1603~1991 464.8 7 文水 Wenshui 37°28′~37°34′ 111°30′~111°35′ 1620~1876 432.8 19 和顺 Heshun 37°11′~37°26′ 113°26′~113°51′ 1223~1359 509.9 13 隰县 Xixian 36°45′~36°47′ 111°11′ 1552~1669 480.0 19 Table 1. The situation of geographical location information and sampling of elite tree in natural population of H. rhamnoides subsp. sinensis in Shanxi
-
表型性状指标主要包括果实横径、果实纵径、果形指数、果柄长、百果质量、种子千粒质量、结实密度、当年枝长、刺长、刺密度。
将同一种群采集的果实充分混匀,采用四分法,50个果实1组,随机抽取3组,共150个果实;利用数显游标卡尺(精度0.01 mm)分别测量各组果实纵径、横径、果柄长。根据果实纵径和横径计算果形指数(果形指数 = 果实纵径/果实横径)。从每个种群中随机抽取500粒果实,分成5组,每组100粒,利用电子天平(精度0.001 g)测定每组果实的质量,取其平均值即为百果质量。将同一种群采集的果实中剥取种子,充分混匀,采用四分法,100粒1组,随机抽取3组,共300粒种子,用电子天平(精度0.001 g)测定每组种子的质量,取其平均值乘以10,即为种子千粒质量。从每个种群内单株的东、西、南、北四个方向分别随机抽取10 cm长的结果枝,测定结果和棘刺数量,选3株优良单株进行重复,计算其平均值即为结实密度和刺密度。从每个种群内单株的东、西、南、北四个方向分别随机抽取、测定当年生枝长,选3株优良单株进行重复,计算其平均值即为当年枝长。从每个种群内单株上随机选取10个棘刺,测量其长度,重复3次,计算刺长。
-
采用SPSS 22.0对数据进行分析。通过单因素方差分析、Duncan新复极差法进行多重比较。计算表型性状的均值、标准差、变异系数(CV),其中,变异系数(CV)= 标准差/均值。
采用相关分析法计算各表型性状间及其与生态因子的Pearson相关系数。对各种群优树的表型性状指标进行主成分分析,鉴于刺长和刺密度越小越好,将刺长、刺密度通过变换倒数方式进行正向转换。采用方差最大化正交旋转方法进行主成分分析[28]。
中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状利用Y值进行综合评价,其计算公式如下:
式中:λ1、λ2、λn分别代表第1主成分、第2主成分、第n主成分的特征值;Y1、Y2、Yn分别代表第1主成分、第2主成分、第n主成分。
采用离差平方和法,根据欧氏距离对各种群优树的主成分综合得分值进行聚类分析,以掌握山西省境内中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状的地理分化特点。
1.1. 试验材料
1.2. 表型性状指标测定方法
1.3. 数据分析
-
中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状的方差分析结果表明:种子千粒质量、果柄长在不同种群间的差异呈显著水平(p < 0.05),其余8个表型性状指标均呈极显著水平(p < 0.01)。可见,中国沙棘优树表型性状在不同群体间存在差异。多重比较结果见表2。
种群
Populations果实横径
Transverse diameter/mm果实纵径
Longitudinal diameter/mm果形指数
Fruit shape index百果质量
Hundred fruit weight/g种子千粒质量
Weight of 1 000-seeds/g右玉 Youyu 5.92±1.02 a 5.39±0.81 a 0.92±0.07 abcd 13.14±6.48 ab 8.25±2.19 a 云州 Yunzhou 6.21±0.42 ab 5.92±0.39 ab 0.95±0.05 d 14.37±3.16 abc 8.10±2.02 a 广灵 Guangling 7.18±0.96 d 6.39±0.36 b 0.89±0.05 abc 21.74±8.33 d 10.21±1.72 ab 五寨 Wuzhai 6.26±0.70 abc 5.65±0.64 ab 0.90±0.01 abcd 14.00±4.89 abc 9.00±2.53 ab 原平 Yuanping 6.92±0.70 bcd 6.06±0.34 ab 0.88±0.05 ab 17.35±5.08 abcd 10.00±2.45 ab 宁武 Ningwu 6.34±0.37 abc 5.64±0.18 ab 0.89±0.07 abc 14.30±1.46 abc 8.75±1.26 ab 岢岚 Kelan 6.4±0.70 a 5.64±0.72 ab 0.93±0.03 bcd 12.85±4.95 a 8.83±2.14 ab 兴县 Xingxian 7.07±0.60 cd 6.20±0.68 ab 0.88±0.05 ab 19.94±5.29 bcd 10.71±2.81 b 文水 Wenshui 7.18±0.74d 6.25±0.87 b 0.87±0.06 a 20.21±7.10 cd 9.32±1.42 ab 和顺 Heshun 6.34±0.84 abc 5.97±0.76 ab 0.94±0.04 cd 15.22±6.40 abcd 8.92±1.61 ab 隰县 Xixian 6.25±0.39 abc 7.28±0.52 c 1.17±0.05 e 20.54±4.14 cd 10.16±1.61 ab 平均 Average 6.52±0.68 6.03±0.62 0.93±0.05 16.69±5.21 9.30±1.98 F值 F value 4.759** 6.991** 42.173** 3.301** 1.963* F检验 Fpr <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 0.001 0.045 种群
Populations果柄长
Fruit stalk length/mm结实密度
Fruit density/
(个·(10 cm)−1)当年枝长
Branch length in current year/cm刺长
Thorn length/cm刺密度
Thorn density/(个·(10 cm)−1)右玉 Youyu 1.37±0.26 a 70.88±12.01 abc 15.04±4.94 ab 3.07±0.51 de 2.43±0.47 b 云州 Yunzhou 1.64±0.44 ab 76.03±13.31 abc 17.36±5.43 abc 2.29±0.63 bcd 2.22±0.64 b 广灵 Guangling 1.36±0.38 a 83.88±27.43 abcd 20.78±7.39 bc 2.58±1.20 cde 2.43±1.27 b 五寨 Wuzhai 1.45±0.25 ab 62.04±20.68 a 14.47±2.48 a 1.53±0.46 ab 2.00±0.85 b 原平 Yuanping 1.56±0.24 ab 86.69±9.85 bcd 17.25±4.15 abc 1.68±0.85 ab 2.25±0.87 b 宁武 Ningwu 1.66±0.38 ab 72.75±16.72 abc 20.85±1.03 bc 2.37±1.27 bcde 2.60±1.26 b 岢岚 Kelan 1.68±0.36 ab 93.29±32.84 cd 12.95±3.10 a 1.07±0.59 a 0.53±0.33 a 兴县 Xingxian 1.59±0.54 ab 75.43±7.70 abc 18.80±5.68 abc 3.07±0.16 de 2.10±0.62 b 文水 Wenshui 1.70±0.44 ab 70.84±17.86 abc 22.34±4.26 c 3.18±0.74 e 2.83±0.98 b 和顺 Heshun 1.62±0.44 ab 63.75±15.14 ab 17.95±6.49 abc 1.80±0.84 abc 2.52±0.76 b 隰县 Xixian 1.90±0.31 b 102.63±25.10 d 21.62±4.28 c 3.19±0.40 e 2.54±0.66 b 平均 Average 1.59±0.37 78.02±18.06 18.13±4.47 2.35±0.70 2.22±0.79 F值 F value 2.221* 4.627** 3.458** 8.901** 3.730** F检验 Fpr 0.022 <0.001 0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:*和**分别表示差异显著(p<0.05)和差异极显著(p<0.01)。表中数据为平均值±标准差,同列不同小写字母表示种群间差异显著(p<0.05)。
Notes: * and ** were respectively significant difference at 0.05 level, high significant difference at 0.01 level. The values in the table are presented as mean ± SD. Different lowercase letters in the same column indicated significant difference at 0.05 level between populations.Table 2. Multiple comparison of phenotypic traits of elite trees in natural populations of H. rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
由表2 可知:隰县种群优树的果实纵径、果形指数、果柄长、结实密度、刺长均最大,百果质量、种子千粒质量较大;广灵种群优树的果实横径、百果质量最大,果实纵径、种子千粒质量、结实密度均较大,果柄最短;兴县种群优树的种子千粒质量最大,果实横径、果实纵径、百粒质量也较大;文水种群优树的当年枝长最长,刺密度最大,果形指数最小;右玉种群优树的果实横径、果实纵径最小,百果质量、种子千粒质量也较小;岢岚种群优树的百果质量、当年枝长、刺长、刺密度均最小;五寨种群优树的结实密度最小;云州种群优树的种子千粒质量最小。
-
中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状的变异情况见表3。研究表明,中国沙棘种群优树的表型性状变异大小因性状而异,10个表型性状的平均变异系数为22.10%,其变化幅度为5.23%~37.42%,以刺密度的变异系数最大,果形指数的变异系数最小。营养生长性状的变异大于生殖生长性状的变异。
种群
Populations果实横径
Transverse
diameter果实纵径
Longitudinal
diameter果形指数
Fruit shape
index百果质量
Hundred fruit
weight种子千粒质量
Weight of
1000-seeds果柄长
Fruit stalk
length结实密度
Fruit
density当年枝长
Branch length in
current year刺长
Thorn
length刺密度
Thorn
density右玉 Youyu 17.22 15.09 7.63 49.32 26.52 19.17 16.94 32.85 16.59 19.44 云州 Yunzhou 6.78 6.68 5.76 21.99 25.00 26.79 17.50 31.28 27.65 28.94 广灵 Guangling 13.43 13.40 5.65 38.31 16.82 28.34 32.70 35.55 46.47 52.17 五寨 Wuzhai 11.19 11.26 0.79 34.93 28.11 17.57 33.33 17.15 30.18 42.43 原平 Yuanping 10.09 5.66 5.75 29.29 24.49 15.56 11.36 24.05 50.86 38.66 宁武 Ningwu 5.86 3.26 8.13 10.20 14.38 22.90 22.98 4.96 53.78 48.65 岢岚 Kelan 11.65 12.68 2.76 38.54 24.19 21.21 35.20 23.90 55.52 61.24 兴县 Xingxian 8.49 11.01 5.22 26.51 26.24 33.97 10.21 30.18 5.30 29.61 文水 Wenshui 10.27 13.93 6.67 35.15 15.20 25.62 25.21 19.08 23.39 34.65 和顺 Heshun 13.21 12.75 4.48 42.05 17.99 27.30 23.76 36.13 47.14 29.93 隰县 Xixian 6.18 7.14 4.70 20.18 15.83 16.44 24.46 19.82 12.44 25.89 平均 Average 10.40 10.26 5.23 31.50 21.34 23.17 23.06 25.00 33.58 37.42 Table 3. Variation coefficients of phenotypic traits of elite trees in natural populations of H. rhamnoides subsp. Sinensis
% 由表3还得知:右玉种群优树的果实横径、果实纵径、百果质量、种子千粒质量变异系数均最大,反映出右玉群体优树的果实性状变异较明显,遗传稳定性较低,果实多样性最丰富;广灵种群优树除种子千粒质量变异系数较小外,其余表型性状的变异系数均较大,反映出该群体表型性状变异分化较明显,遗传稳定性较低。隰县种群优树的10个表型性状的变异系数均较小,反映出该种群优树表型性状遗传稳定性较高,多样性相对较单一。
-
中国沙棘优树表型性状间的相关分析结果(表4)表明:中国沙棘优树的10个表型性状指标间存在不同程度的相关性,其中,果实横径与果实纵径、百果质量、种子千粒质量、当年枝长均呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关,与果形指数、结实密度呈极显著(p < 0.01)负相关;果形指数与果实纵径、果柄长、结实密度呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关,与果实横径呈极显著(p < 0.01)负相关;种子千粒质量与果实横径、果实纵径、百果质量呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关;当年枝长与刺长、刺密度呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关;刺密度与果实纵径、百果质量、当年枝长、刺长呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关。
表型性状
Phenotypic traits果实横径
Transverse
diameter果实纵径
Longitudinal
diameter果形指数
Fruit shape
index百果质量
Hundred fruit
weight种子千粒质量
Weight of
1000−seeds果柄长
Fruit stalk
length结实密度
Fruit
density当年枝长
Branch length
in current year刺长
Thorn
length刺密度
Thorn
density果实横径
Transverse diameter1.000 果实纵径
Longitudinal diameter0.612** 1.000 果形指数
Fruit shape index−0.319** 0.551** 1.000 百果质量
Hundred fruit weight0.884** 0.872** 0.115 1.000 种子千粒质量
Weight of 1000−seeds0.528** 0.585** 0.137 0.602** 1.000 果柄长
Fruit stalk length−0.033 0.285** 0.380** 0.092 0.115 1.000 结实密度
Fruit density−0.308** −0.015 0.320** −0.183 −0.168 0.023 1.000 当年枝长
Branch length in current year0.285** 0.316** 0.092 0.332** 0.136 0.158 −0.059 1.000 刺长
Thorn length0.123 0.285** 0.214* 0.248** 0.068 0.216* −0.002 0.466** 1.000 刺密度
Thorn density0.227* 0.253** 0.075 0.298** 0.116 0.078 −0.152 0.322** 0.507** 1.000 注:*:p < 0.05;**:p < 0.01。下同。
Notes: *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01. The same as below.Table 4. Correlation analysis of phenotype traits of elite trees in H. rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
-
中国沙棘优树表型性状与生态因子间的相关分析结果(表5)表明:中国沙棘优树的表型性状与生态因子间存在不同程度的相关性,其中,果实横径、果实纵径、百果质量、种子千粒质量、当年枝长与海拔因子呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关;果实纵径、果形指数、果柄长、当年枝长与纬度因子呈极显著(p < 0.01)负相关;果形指数与年降水量呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关。
表型性状
Phenotypic traits纬度
Latitude经度
Longitude海拔
Altitude年平均降水量
Precipitation果实横径 Transverse diameter −0.027 0.039 0.357** −0.165 果实纵径 Longitudinal diameter −0.411** −0.231* 0.302** 0.184 果形指数 Fruit shape index −0.467** −0.323** −0.005 0.389** 百果质量 Hundred fruit weight −0.194* −0.096 0.378** −0.021 种子千粒质量 Weight of 1000−seeds −0.159 −0.105 0.339** 0.075 果柄长 Fruit stalk length −0.342** −0.274** −0.024 0.236* 结实密度 Fruit density −0.148 −0.216* 0.053 0.017 当年枝长 Branch length in current year −0.250** −0.133 0.274** 0.016 刺长 Thorn length −0.186 −0.295** 0.126 −0.049 刺密度 Thorn density −0.157 0.002 0.094 0.020 Table 5. Correlation analysis between phenotype traits and ecological factors in elite trees of H. rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
-
对中国沙棘天然种群优树的表型性状进行主成分分析,结果(表6),得到3个特征根大于1的主成分,第1主成分中百果质量、果实纵径、当年枝长载荷度较高,主要表征的是果实大小性状和当年生长量,贡献率为46.15%;第2主成分中果形指数、结实密度载荷度较高,主要表征的是果实的长宽比和结实性状,贡献率为26.13%;第3主成分中刺密度、种子千粒质量、刺长载荷度较高,主要表征的是棘刺的性状和种子大小性状,贡献率为15.38%。上述3个主成分的累积方差贡献率为87.66%,已能反应中国沙棘优树表型性状10个测定指标的绝大多数信息,故选取前3个主成分为中国沙棘优树表型性状的重要主成分。
表型性状
Phenotypic traits主成分 Component 1 2 3 果实横径 Transverse diameter 0.67 −0.51 0.50 果实纵径 Longitudinal diameter 0.90 0.38 −0.02 果形指数 Fruit shape index 0.35 0.78 −0.43 百果质量 Hundred fruit weight 0.95 −0.12 0.25 种子千粒质量 Weight of 1000−seeds 0.77 −0.01 0.53 果柄长 Fruit stalk length 0.38 0.69 −0.23 结实密度 Fruit density 0.40 0.76 0.30 当年枝长 Branch length in current year 0.87 −0.17 −0.24 刺长 Thorn length −0.67 0.40 0.52 刺密度 Thorn density −0.51 0.58 0.55 特征值 Eigen value/λ 4.62 2.61 1.54 贡献率 Contributive percentage/% 46.15 26.13 15.38 Table 6. The PCV of phenotypic traits of elite trees in natural populations of H. rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
Y1、Y2、Y3主成分的函数式是根据样本成分相关矩阵的因子得分矩阵得出:
Y1=0.349X1+0.112X2−0.174X3+0.264X4+0.349X5−0.076X6+0.146X7 +0.046X8+0.092X9+0.120X10
Y2=−0.196X1+0.212X2+0.366X3+0.001X4−0.028X5+0.304X6+0.237X7 +0.065X8−0.020X9+0.049X10
Y3=−0.059X1−0.044X2−0.094X3−0.019X4+0.150X5−0.020X6+0.228X7−0.240X8+0.385X9+0.415X10
式中:X1代表果实横径;X2代表果实纵径;X3代表果形指数;X4代表百果质量;X5代表种子千粒质量;X6代表果柄长;X7代表结实密度;X8代表当年枝长;X9代表刺长的倒数;X10代表刺密度的倒数。
通过公式(1),计算得出中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状的综合评价结果见图1。结果表明:中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状的综合得分从高到低依次为隰县、岢岚、广灵、原平、兴县、文水、云州、宁武、右玉、和顺、五寨,说明隰县种群优树的表型性状表现最佳,五寨种群优树的综合表型性状最差。为掌握山西省境内中国沙棘优树的表型性状地理分化特点,进一步将主成分综合得分进行聚类分析,结果见图2。
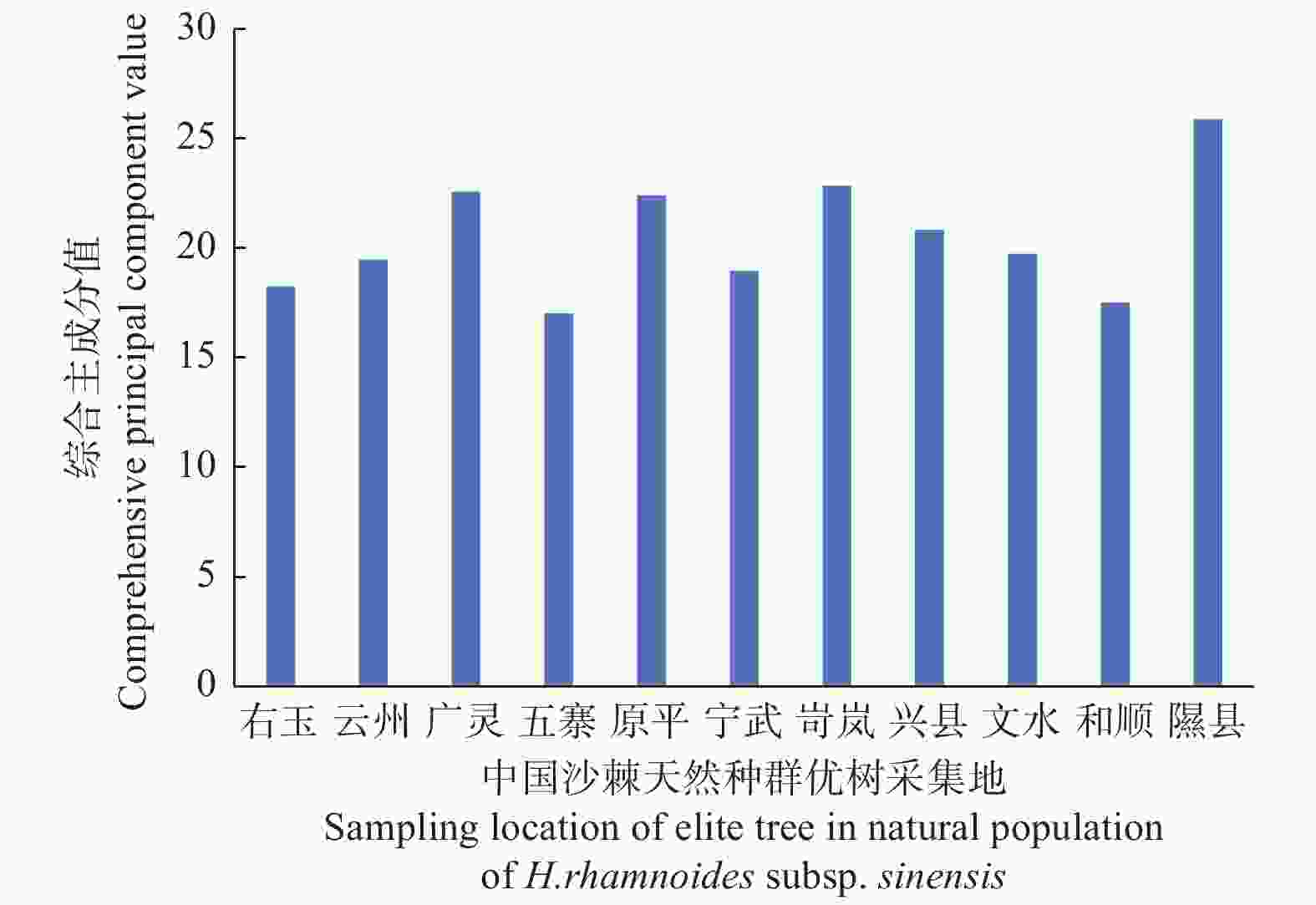
Figure 1. Comprehensive principal component scores of elite trees in natural populations of H. rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
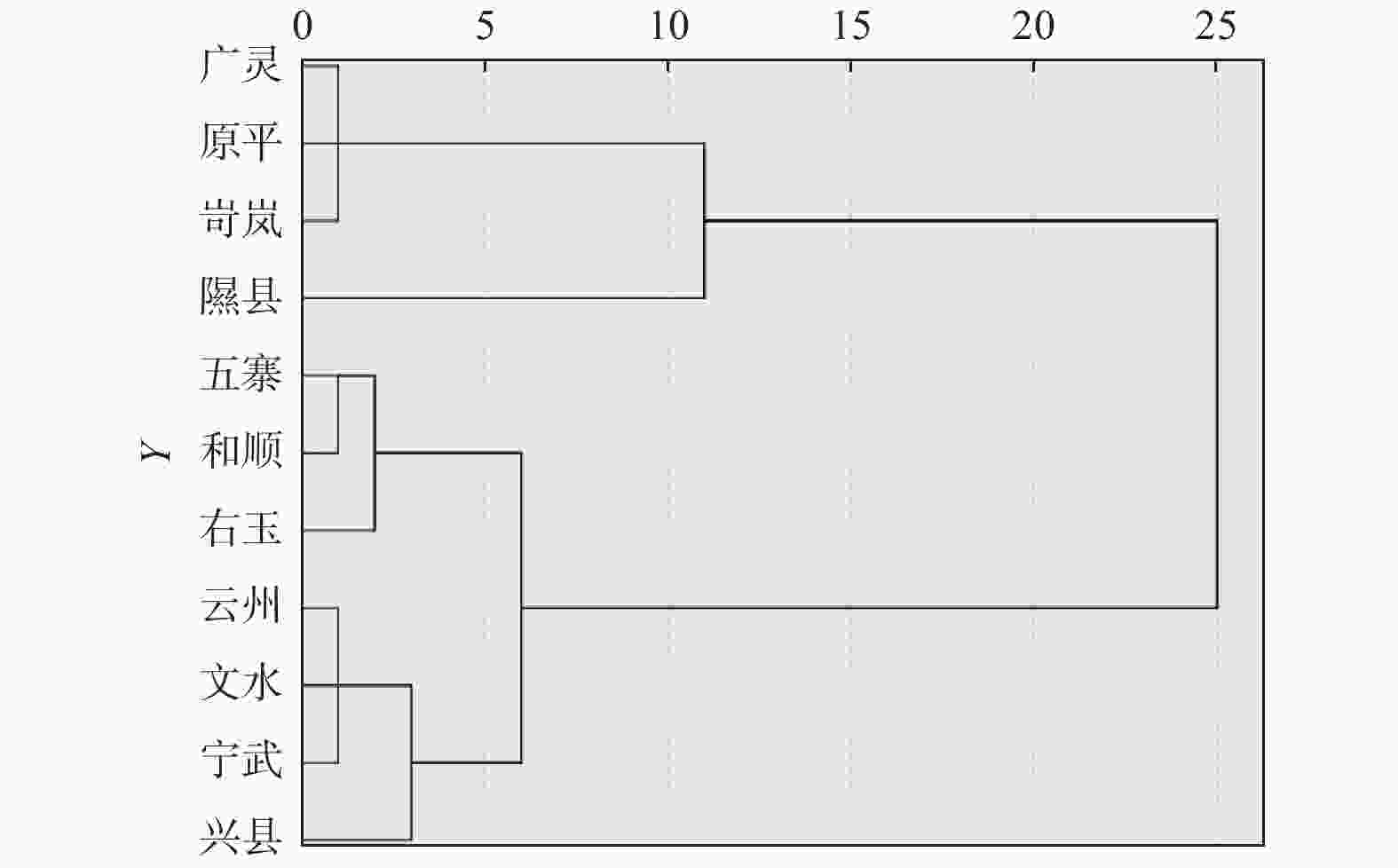
Figure 2. Cluster analysis of phenotypic traits of elite trees in natural populations of H. rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
聚类分析结果表明,在距离系数为5时,可将11个中国沙棘天然种群优树分为4类,第1类为隰县种群优树,综合性状表现最好;第2类分别为广灵、原平、岢岚种群优树,综合表现较好;第3类分别为云州、文水、宁武、兴县种群优树,综合表现一般;第4类分别为五寨、右玉、和顺种群优树,综合表现较差。
2.1. 中国沙棘天然种群优树的表型性状差异性比较
2.2. 中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状的变异特征
2.3. 中国沙棘优树表型性状间的相关性分析
2.4. 中国沙棘优树表型性状与生态因子间的相关性
2.5. 中国沙棘优树表型性状的主成分分析
-
丰富的优良种质资源是林木育种研究重要的物质基础,其中,表型性状分析对揭示基因型差异以及鉴定种群生态学分析具有重要意义[23]。生物的变异和多样性是开展育种工作的前提,变异系数可以反映性状值的离散特征,变异系数越大,性状值的离散程度越大,表型多样性越高;相反,变异系数越小,说明该种群的性状离散程度越低,物种多样性越低[12]。有研究表明,植物群体间的变异程度能反映出植物本身对环境的适应程度,变异系数越大,说明植物适应环境的范围越广[29]。
本研究发现,山西省中国沙棘天然种群优树间存在丰富的表型变异,平均变异系数为22.10%,其中,刺密度的变异系数最大(37.42%),果形指数的变异系数最小(5.23%),营养生长性状的变异大于生殖生长性状的变异。黄铨等[24]研究发现,山西省关帝山的中国沙棘每个性状都有很大幅度的变异,其中,营养器官的变异多大于生殖器官的变异,而在生殖器官中,果柄长度和鲜果百粒质量的变异又大于其它性状。吴琼等[25]研究发现,山西省中国沙棘天然种群各表型性状的平均变异系数介于3.1%~26.5%,其中,营养性状变异幅度最大,种子性状最小。本研究结果与其一致,可能是因为营养器官主要通过光合作用为植物提供养分,容易受到外界环境因素的影响,变异性较强;而果实属于生殖器官,主要受自身遗传因素控制,性状相对稳定,这也保证了物种遗传上的相似性和稳定性[6]。
另外,本研究还发现,中国沙棘优树的同一性状在不同种群的变异幅度存在差异性。余天蓝等[23]在对新疆6个居群野生沙棘果实性状多样性研究也得出类似结论。这在一定程度上也表明,生长环境的异质性可能是导致中国沙棘种群优树表型变异的主要原因。
-
不同植物对环境因子的适宜机制和敏感程度的差异导致其呈现不同的地理变异规律[8]。中国沙棘优树表型性状相关分析表明,种子千粒质量与果实横径、果实纵径、百果质量呈极显著(p < 0.01)正相关,表明沙棘种子大小与果实大小存在关系,果实的纵、横径越大,种子也越大,该研究结果与吴琼[30]对中国沙棘表型性状相关性分析结论一致。中国沙棘优树表型性状与生态因子间的相关分析显示,果形指数与纬度因子呈极显著负相关,表明随纬度降低,果实纵径越大,果形指数增大;果实横径、果实纵径、百果质量、种子千粒质量与海拔因子呈极显著正相关,表明随海拔升高,沙棘果实、种子增大,该研究结果也与吴琼[30]对中国沙棘表型性状相关性分析结论一致。通常情况下,植物表型性状的地理变异比较复杂,而且因物种而异,如长柄扁桃种群表型变异主要受年平均气温、纬度和无霜期3个主要地理气候因子影响[11],无患子表型性状的变异与地理纬度和年平均气温2个主要因子密切相关[28],川西云杉种实性状存在经度和纬度并存的变异模式[29]。本研究结果表明,中国沙棘天然种群优树的表型性状变异与地理纬度和海拔2个主要因子密切相关。
由于分布和环境条件等因子的综合作用,植物会形成连续变异、不连续变异以及随机变异等多种地理变异模式[31]。主成分分析和聚类分析结果发现,遗传距离大致在5时,分界线将山西省11个中国沙棘种群优树分为4类,各种群并未严格按照地理距离而聚类,说明山西省中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状未形成连续变异,具有随机变异的特点。吴琼等[25]研究也发现,山西省境内中国沙棘没有表现出明显的地理梯度变异式样,表型性状分化有多态性的特点。可能是由于中国沙棘主要分布在深山沟壑中,种群间大多受吕梁山、太行山等高大山脉的隔离,种子和花粉难以在种群间传播,即使地理距离较近的种群间难以进行基因交流,增加了各种群独立分化的机会。
-
沙棘是集水土保持、医药保健、工业日化等为一体的多功能生态树种,在我国生态建设和乡村振兴中发挥着巨大的作用。中国沙棘在山西省境内分布跨度大,生长环境条件复杂,通过长期的地理隔离、自然选择,使得山西省中国沙棘种群优树间存在丰富的变异,为中国沙棘遗传改良奠定了重要物质基础。为了充分保护和利用现有中国沙棘天然资源,有效地进行遗传改良,培育优质、高产及功能性新品种,建议如下:(1)中国沙棘表型变异主要与纬度和海拔相关,尽可能丰富这些因子的采样范围,进行随机采样,同时增加采样数和叶片、种子的评测指标,使研究更系统、全面,才能更有效地开展中国沙棘的保护和利用工作;(2)开展生态遗传学研究,将形态学、分子标记和地理生态结合分析种群遗传多样性,掌握各种群的亲缘关系;(3)加强对现有中国沙棘天然种群和优良单株的保护力度,通过收集种质资源,建立基因库,有效避免采种对现有遗传资源的破坏。
3.1. 中国沙棘优树表型性状变异的多样性
3.2. 中国沙棘种群优树间表型性状与生态因子的关系
3.3. 沙棘优良种质资源的保育与利用
-
山西省中国沙棘天然种群优树间存在丰富的表型变异,平均变异系数为22.10%,营养生长性状的变异大于生殖生长性状的变异,其中,隰县中国沙棘种群优树的果实纵径、结实密度最大,表型性状的变异系数较小,综合性状表现最好,可参考作为中国沙棘优良种质资源收集的重点区域。中国沙棘天然种群优树的表型性状变异与地理纬度和海拔2个主要因子密切相关。山西省中国沙棘天然种群优树表型性状未形成连续变异,具有随机变异的特点。以上研究为中国沙棘优良种质资源收集和品种创制奠定了重要物质基础,也为其栽培区划提供了技术参考。






 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
