-
油橄榄(Olea europaea L.),也称齐墩果,属木樨科(Oleaceae)木樨榄属(Olea)的常绿阔叶乔木,果实形似橄榄,果肉内富含油脂[1]。甘肃省陇南地区自1975年开始对油橄榄进行规模引种,经过数十年的艰苦探索和研究试验,油橄榄已在该地区能正常生长且获得些许产量[2];但由于缺乏对良种壮苗优育优选的认识,现培育出的幼苗存在移栽成活率较低、缓苗期长、树势较弱等问题。本研究针对油橄榄扦插容器苗的主根徒长又较为粗大、须根极少、根系盘绕、畸形等现象开展化学制剂控根试验,使其形成健康又发达的根团,从而解决根系畸形导致油橄榄苗木质量差且缓苗期长等问题[3-5]。
化学制剂控根技术是将Cu制剂或Zn制剂涂于育苗容器的内壁和底面上,通过Cu2+或Zn2+离子与根尖的接触,杀死根尖,从而达到根的顶端修剪目的,抑制其生长,刺激并诱发更多的侧根向四周伸展,也可以防止根系缠绕导致的畸形,生成舒展又发达的根团[6-7]。Vitor等研究发现Cu制剂能促进葡萄(Vitis vinifera L.)幼苗根系直径增长,降低根冠比,并有利于葡萄幼苗根系结构生长[8];而吕昕等的研究结果表明幼苗的根系构型对其后期的生长,养分的吸收,以及移栽后的成活率都有直接影响[9],James等发现Cu制剂可有效改变长叶松(Pinus palustris)幼苗的根系形态,显著增加根系生物量[10],Tsakaldimi等经试验证明:人为的改变冬青栎(Quercus ilex L.)苗株生长的环境因素或施以不同的培育措施都会改变苗株根系的构型[11]。Faye研究发现Cu制剂可以有效的缩短火炬松(Pinus taeda L.)侧根长度,改变新根生长点的分布,增加根系中上部的新根着生点,使根系生长更接近于自然状态[12]。Lequeux等表明当Cu2+浓度高达50μmol·L-1时可抑制拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)主根生长并能增加短侧根的密度[13]。将Cu制剂配成一定浓度,选用乳胶漆作为附着剂,Cu制剂处理剂量与侧根增加数目是成正比的[14-15]。可见,科学的控根措施可改善根系生长发育环境[16],促进苗木根系对养分吸收,并提高苗木质量。
目前,国内尚无关于采用化学控根制剂干扰油橄榄扦插苗主根的发展及促进侧根生长的相关研究;国外也未见关于化学控根制剂对油橄榄根系等方面的相关报道。鉴于此,本试验针对油橄榄容器苗根系发育不良等问题,采用4种不同浓度的CuSO4制剂及ZnSO4制剂对油橄榄2年生容器苗进行控根试验,试图阻止苗木根系在容器内的畸形生长,以期为实现油橄榄育苗工厂化、规模化生产提供参考。
HTML
-
试验在甘肃省陇南市武都区两水镇油橄榄育苗地进行,该圃地土层肥沃,立地条件较好,日照充足,年平均气温14.7 ℃,绝对最高气温40 ℃,最低气温-8.6 ℃,年日照时数1 911.7 h,全年无霜期为150~270 d,年降水量474~900 mm,年平均湿度61%~71%。
-
于2015年3月底挑选2年生长势基本一致的油橄榄硬枝扦插苗移栽,品种为‘鄂植8号’,选择普通营养钵20 cm×20 cm(底×高)为试验容器,供试基质为耕作层表土。
-
采用随机区组设计,共设9个处理,每处理30盆苗(表 1);分别将硫酸铜(CuSO4)、硫酸锌(ZnSO4)2种制剂配制成不同浓度与乳胶漆充分混合后,涂刷在营养钵的内壁与底部,只涂乳胶漆作为对照(CK),晾干后填装耕作层表土备用。于2015年3月底将油橄榄苗木移栽后,对试验苗株仅进行日常灌溉管理,不采取整形修剪及施肥等田间管理措施。
控根制剂
Root control agent浓度Concentration/(g·L-1) 0 20 60 120 200 CuSO4 CK A1 A2 A3 A4 ZnSO4 B1 B2 B3 B4 Table 1. Different kinds and concentration of root control agents
-
生产量:自2015年7月至11月于每月15日固定选择15株苗株,定期测量苗高、地径、枝条生长量;生物量:每处理随机抽取3株,将植株完整取出,清理干净,将地上部分和地下部分进行分离,置于105℃下烘干至恒质量,分别称得干质量;
-
2015年11月底对植株进行根系形态参数的测定,使用专业根系形态学和结构分析系统Delta-T Scan根系分析系统采用高分辨率的平板扫描仪进行扫描分析。将植株在根颈处剪断,并置根系在轻缓的流水下冲洗干净,再将根放入分析浅皿,加入少量水,使根系均匀分展开,用扫描仪获取清晰的根系图像。分析侧根(1.0 mm≤D≤2.5 mm)的长度、根系表面积、根系体积、根尖数、根系直径等指标。
-
可溶性蛋白质含量测定采用考马斯亮蓝G250(Bradford法)测定;可溶性糖测定采用蒽酮比色法;叶绿素含量测定采用乙醇丙酮混合液法。
-
试验数据采用Excle 2007做基础整理分析,运用软件Spss Statistics17.0针对数据进行方差分析以及相关性分析。
1.1. 试验地概况
1.2. 试验材料
1.3. 试验设计
1.4. 调查内容及方法
1.4.1. 生态指标测定
1.4.2. 根系形态参数的测定
1.4.3. 叶片生理指标的的测定
1.5. 数据分析
-
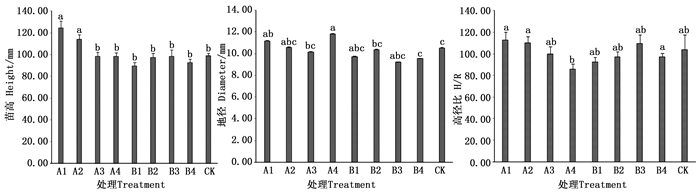
苗高与地径的年生长量是油橄榄苗株生长势的重要指标,经不同浓度的控根制剂处理后的苗高、地径具有明显差别。Cu制剂A1处理的苗高年生长量均高于其他处理以及对照,比处理A4高出26.18 cm,比对照高大约20.60%;方差分析结果显示,Cu制剂A1和A2处理间无显著差异性,但同其它处理及CK之间差异显著;而Zn制剂的各处理间并无显著差异。由图 1可知,A1和A2处理的苗高年生长量相比Zn制剂各处理有明显优势,说明施用Zn制剂对2年生的油橄榄容器苗的苗高并无显著效果,而质量浓度为60和200 g·L-1的Cu制剂即A1与A4处理可有效促进油橄榄苗高年生长量。在相同质量浓度下,Cu制剂的各处理的地径年生长量均高于Zn制剂,如处理A4比B4粗2.27 cm;而Zn制剂的各处理均低于CK。方差分析显示,CK仅与A1、A4处理之间有显著差异性,Cu、Zn制剂各处理的地径年生长量排列依次为:A4>A1>A2>CK>B2>A3>B1>B4 >B3。可见,质量浓度为200 g·L-1的Cu制剂可以有效的促进油橄榄容器苗地径的年生长量。
油橄榄苗木的高径比值越大,说明该苗株越细越高,直接影响苗木成活率,移栽后长势也较弱[4]。经不同质量浓度Cu制剂处理后的苗株高径比值最小的为A4处理,并与其他处理间差异性显著,最大的为A1处理;Zn制剂的高径比最大的为B3处理,但与CK差异不显著。
-
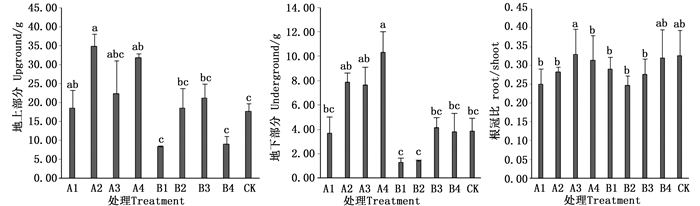
不同的控根制剂对2年生的油橄榄容器苗生物量影响差异较大。Cu制剂处理的苗株地上部分干质量生物量最大为A2处理,达到34.82 g,A4处理次之,均高于CK;而Zn制剂的B1处理和B4处理的生物量都低于CK,生物量最小的是B1处理,仅为8.33 g,比CK小52.61%。经方差分析,对于地上部分生物量,处理A1、A2和A4与CK间存在显著差异性,但这3个处理间并无显著差异。对地下部分生物量结果分析可得:处理A4的地下部干质量生物量为最大,达到10.33 g,A2处理次之,B1处理最小,仅为1.32 g。Cu制剂处理A2、A3和A4之间差异不显著,Zn制剂的地下部分生物量各处理间无显著差异。
由图 2可知,根冠比最大的为处理A3,方差分析表明:A3、B4处理和CK之间不存在显著差异性;但同其它处理之间差异性显著。由2种控根制剂对油橄榄2年生容器苗生物量积累的影响可以发现:Cu制剂质量浓度为60和200 g·L-1的A1和A4处理显著提高了油橄榄苗的地上及地下生物量的积累。
-
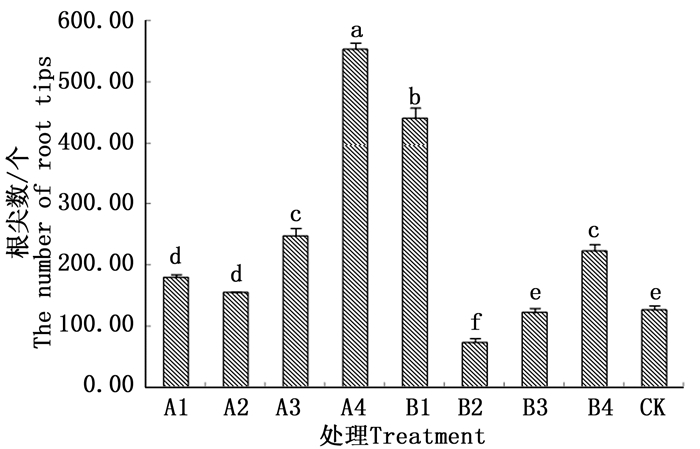
Cu制剂可刺激油橄榄容器苗的新根着生,各处理的根尖数相比CK均有所增加。根尖数最多的是处理A4,达到553个,与CK相比增加了3倍之多;而CK的根尖数仅有126个,最少的处理A2也比CK增加了23.02%。Zn制剂对根尖数的作用不明显,仅处理B1和处理B4高于CK的根尖数;根尖数最少的是B2处理,仅73个。由方差分析可知,Cu制剂各处里均与CK间差异性显著;而A1和A2处理间无显著差异,但与其余各处理差异性显著。Zn制剂B3处理与CK之间无显著差异,而其余各处理之间差异性均为显著。据此说明Cu制剂的各处理均对油橄榄容器苗新根着生起到促进作用;而Zn制剂的B2及B3处理对苗株新根着生起到抑制作用。
-
由表 2可知,Cu制剂处理对油橄榄苗的侧根直径影响较Zn制剂大,A3处理的侧根直径最大,是CK的1.74倍,而直径最小的处理B4,比CK增加了9.85%,CK与Cu制剂各处理间差异显著。Cu制剂对侧根长度作用也明显优于Zn制剂,而Zn制剂对油橄榄侧根长度有明显的抑制作用,各处理均小于CK。A2处理和A4处理的侧根长度大于CK,其中A4处理的侧根长度比CK高出21.63%。
处理Treatment 直径Diameter /mm 长度Length/cm 表面积Superficial area /mm2 体积Volume /mm3 A1 2.03±0.04b 7.07±0.55c 143.99 ±11.93cd 510.15±13.64c A2 1.76 ±0.04c 11.84 ±0.63ab 263.14 ±32.94ab 712.98 ±46.22b A3 2.30±0.05a 8.27 ±0.25c 296.78 ±34.57a 1 261.34 ±137.97a A4 1.66±0.12cd 13.10 ±0.42a 280.80 ±53.65ab 801.04 ±43.79b B1 1.73±0.05d 4.79 ±0.28d 134.40 ±8.20cd 469.35 ±25.14c B2 1.55±0.03cd 1.48 ±0.04e 42.62 ±0.43e 156.18 ±3.89e B3 1.60±0.09cd 4.32 ±0.31d 112.51 ±13.67de 432.19 ±20.79c B4 1.45±0.03de 4.97 ±0.74d 111.03 ±16.19de 258.52 ±18.47de CK 1.32±0.07e 10.77 ±0.29b 201.28 ±10.60bc 361.01 ±5.57cd 注:数据为平均值±标准误;不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。
The figures in the table are mean±standard error, the different small letter indicates significance at 0.05 level.Table 2. Effect of Cu、Zn preparation on lateral root indicators in container seedlings of olive
Zn制剂各处理的侧根表面积均小于CK,其中处理B1处理的侧根表面积值最大,仅达到134.40 mm2,比CK小33.23%。Cu制剂的侧根表面积最大是处理A3为296.78 mm2,处理A2次之。数据显示,Cu制剂各处理的侧根系体积均高于CK;除处理A1外,其余各处理与CK均存在显著性差异;A2与A4间无差异,但与A3存在显著差异性。在Zn制剂的所有处理中,根系体积最大为B1处理,仅达到469.35 mm3,处理B1和B3的根系体积均大于CK,试验结果表明:质量浓度为120 g·L-1的Cu制剂能明显的抑制侧根系长度,对根系的直径、表面积和体积有明显的促进作用;而不同Zn制剂处理对苗木侧根各指标有一定的抑制作用,其中质量浓度为60 g·L-1的Zn制剂对侧根长度、表面积的抑制作用最为显著。
-
表 3是苗高、地径、枝条生长量与侧根各指标的相关性分析结果。经相关性分析可知,苗高与根尖数、根直径、根体积都呈负相关性;地径和枝条生长量与侧根长度呈显著极正相关(P < 0.01),与苗高相比,枝条生长量与侧根长度的相关性更大,而枝条生长量与苗高呈极显著正相关关系。地径与根尖数、长度以及根系表面积均呈现极显著正相关性,其中,地径与侧根表面积显著正相关(P < 0.05),枝条生长量与侧根表面积也呈显著正相关(P < 0.01)。根尖数与根系长度、根系表面积呈极显著正相关,根系直径与根体积也呈现正相关性,相关系数r=0.707,即根系直径随根系体积的增加而增加。根系长度与表面积的相关系数r=0.810,呈显著正相关,即根系长度随根系表面积的增大而增长。
项目Items 苗高
Height地径Base
diameter枝条生长量
Branch growth根尖数Tips 直径Diameter 长度Length 表面积SA 体积
Volume苗高Height 1 0.449** 0.563** -0.100 -0.191 0.243 0.115 -0.088 地径Base diameter 1 0.579** 0.382** -0.066 0.587** 0.540** 0.210 枝条生长量
Branch growth1 0.174 -0.200 0.543** 0.355* 0.009 根尖数Tips 1 -0.116 0.563** 0.493** 0.232 直径Diameter 1 -0.228 0.148 0.707** 长度Length 1 0.810** 0.271 表面积SA 1 0.672** 体积Volume 1 **. 在0.01水平(双侧)上极显著相关,*. 在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。
**Significant correlation at the 0.01 level(bilateral), *signficant correlation at the 0.05 levelTable 3. Correlation analysis of root indicators with on the ground increment
-
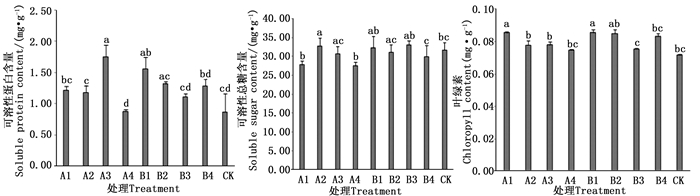
可溶性蛋白含量是植物体总代谢的重要指标,是筛选抗性的重要营养物质之一。由图 4可知,Cu制剂的A3处理的可溶性蛋白质含量最高,与CK间差异性显著,而A4处理则比CK小1.37%,与CK间并无显著差异。Zn制剂的B1处理的可溶性蛋白含量仅次于A3处理,与CK间差异显著。可见,针对可溶性蛋白含量的最优处理为A3,即浓度为120 g·L-1的Cu制剂。

Figure 4. Effect of Cu、Zn preparation on physiological indicators of olive leaves in container seedlings
可溶性糖作为反映苗木质量的重要指标,也反映出不同控根制剂处理对苗株营养的增益情况。质量浓度为120 g·L-1的Zn制剂B3处理叶片的可溶性糖含量最高,其次为60 g·L-1的Cu制剂A2处理;但B3处理与CK间并无显著差异性,而与A2处理同CK间存在显著差异性。因此质量浓度为60g·L-1的Cu制剂更利于植株的生长。
2种不同的控根制剂均可提高油橄榄的叶绿素含量,该指标最高为处理A1,其次为处理B1。经方差分析,处理A1、B1与CK间差异性均为显著,且各处理的叶绿素含量均大于CK。由上可知,质量浓度为20 g·L-1的Cu制剂和20 g·L-1的Zn制剂均有利于提高植株的叶绿素含量。
2.1. Cu、Zn制剂处理对油橄榄容器苗生长表现的影响
2.2. Cu、Zn制剂处理对油橄榄容器苗生物量积累的影响
2.3. Cu、Zn制剂对油橄榄容器苗根系形态参数的影响
2.3.1. Cu、Zn制剂对油橄榄容器苗的根尖数的影响
2.3.2. Cu、Zn制剂对油橄榄容器苗根系发育的影响
2.4. 苗木生长量与根系指标的相关性分析
2.5. Cu、Zn制剂对油橄榄容器苗叶片生理指标的影响
-
化学控根技术在实际生产中操作简单,成本低廉,对育苗环境要求相对较低。通过试验可发现,油橄榄2年生容器苗生长及其根系发育对化学控根制剂表现出明显的响应差异。Cu制剂质量浓度分别为20和60 g·L-1的A1和A2处理对油橄榄容器苗高有明显的促进作用;A4处理可有效的促进油橄榄容器苗地径的生长。Zn制剂浓度为120 g·L-1时高径比优于同处理的其它各浓度,但Cu制剂的A4处理苗株高径比为最佳。Zn制剂对地径生长量作用不显著,而Cu制剂A4处理可有效的促进油橄榄容器苗地径的生长。质量浓度为60和200 g·L-1的Cu制剂A1和A4处理可显著提升油橄榄苗的地上及地下鲜质量,120 g·L-1的Cu制剂A3处理根冠比最佳;但是Zn制剂处理的苗株地上和地下部分生物量积累并不明显,针对Zn制剂对苗木造成胁迫的原因有待进一步研究。
苗木根系对化学控根制剂的反应也不相同,Cu制剂的各处理均可增加油橄榄容器苗根尖数,而根尖数最多的是Cu制剂的A4处理浓度为200 g·L-1;但Zn制剂的B2处理和B3处理对油橄榄容器苗的新根着生起到抑制作用。Cu制剂对侧根长度作用明显优于Zn制剂;Zn制剂各处理均小于CK。Cu制剂质量浓度为120 g·L-1的A3处理能明显的抑制侧根系长度,对根系的直径、表面积和体积有明显的促进作用。综上所述,Cu制剂在120和200 g·L-1浓度时可达到控制主根过长生长、促进侧根增加、形成发达根团的目的,效果最佳。油橄榄容器苗地上部分的生长与根系的发育存在密切的关系,通过对苗株各项指标的相关性分析得出以下结论:地径和枝条生长量与侧根长度呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),与苗高相比,枝条生长量与侧根长度的相关性更大。地径与侧根表面积显著正相关(P < 0.05),而枝条生长量与侧根表面积也呈显著正相关(P < 0.01)。研究显示,苗木叶片养分储存量随着控根制剂以及浓度的不同也发生变化,质量浓度为120 g·L-1的Cu制剂的可溶性蛋白质含量最高,质量浓度为20 g·L-1的Cu制剂可有效提高叶片的叶绿素含量。
-
合理的控根技术可使油橄榄幼苗形成健康又发达的根团,避免幼苗质量差且缓苗期过长等问题,是解决容器育苗侧根稀少,主根陡长的有效途径。试验证明:Cu制剂在120和200g·L-1浓度时可达到控制主根过长生长、促进侧根增加、形成发达根团的目的,且效果显著。本试验仅研究了质量浓度为20~200 g·L-1 Cu制剂和20~200 g·L-1 Zn制剂对2年生油橄榄容器苗控根效果的影响。针对Zn制剂的最佳质量浓度以及如何降低药剂对苗木的影响,且更好地控制化学制剂残留与控根效果之间的矛盾是探索的新方向,是油橄榄育苗化学制剂控根技术下一步的研究重点。








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: