-
芍药(Paeonia lactiflora Pall.)又名将离、离草、余容、没骨花、犁食等[1],与牡丹(Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.)同科同属。芍药为多年生草本,牡丹为多年生小灌木[2-3]。芍药花大色艳,花型丰富,具有很强的观赏价值,既可作园林绿化植物,也可以作盆花和切花[4];花及根具有补血敛阴、柔肝止痛、养阴平肝的功效[5],是一味重要的中药材。芍药在我国东北、华北、陕西及甘肃南部等地区均有分布[6],对极端环境因子有很强的耐受性[7],极具推广价值。
目前,我国的油料作物生产受到各方面因素影响,产量远不及欧美发达国家,食用植物油的人均占有量不到世界平均水平的70%[8]。中国食用油进口量由2000年的187.00万吨增长到2013年的810.00万吨,增长幅度达333.16%,中国所消费的食用油一半以上需要从国外进口或利用进口植物油籽加工,而且近几年进口量增加的趋势越加明显[9]。2011年3月22日,牡丹籽油被批准作为新资源食品(卫生部公告2011年第9号)。无论从遗传,还是外观、形态方面,芍药都与牡丹有很强的相似性,特别是芍药具有非常强的结实力,极具开发成新型油料作物的潜力。目前,仅见马广莹等[10]、宁传龙[11]等、罗婧[12]从芍药籽油理化性质、提取工艺和营养成分等方面进行了研究,查素娥等[13]对6个芍药品种含油率和4种脂肪酸成分进行了简要的分析。本文对芍药36个品种和1个自然居群的种子进行了油脂提取,并对其籽油脂肪酸成分进行了对比分析,旨在为芍药籽油进一步开发利用提供参考。
HTML
-
本文中36个品种和1个自然居群的芍药种子,分别采自山东省菏泽市曹州牡丹园和河北省张家口市赤城县大海陀山(表 1)。曹州牡丹园区属暖温带季风性气候,年平均气温13.9℃,年均降水量625 mm,海拔68~37 m,砂质壤土;大海陀山属温带大陆性季风气候,昼夜温差较大,年平均气温1.0~4.5℃,年均降水量480~607 mm,最高海拔2 241 m。芍药自然居群主要分布在海拔1 300 m左右的南坡上,棕壤土。
样品号Number 中文名Chinese name 拉丁学名Scientific name 产地Locality 1 ‘大地皆春’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Dadijiechun’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 2 ‘春晓’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Chunxiao’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 3 ‘粉盘藏珠’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Fenpancangzhu’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 4 ‘大红赤金’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Dahongchijin’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 5 ‘红花露霜’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Honghualushuang’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 6 ‘朱砂判’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Zhushapan’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 7 ‘烈火金刚’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Liehuojingang’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 8 ‘墨紫含金’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Mozihanjin’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 9 ‘圆叶锦球’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Yuanyejinqiu’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 10 ‘艳丽’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Yanli’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 11 ‘锦山红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Jinshanhong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 12 ‘盘托绒花’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Pantuoronghua’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 13 ‘赵园红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Zhaoyuanhong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 14 ‘长茎红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Changjinghong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 15 ‘奇花露霜’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Qihualushuang’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 16 ‘蝶落粉池’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Dieluofenchi’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 17 ‘莲台’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Liantai’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 18 ‘东海朝阳’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Donghaichaoyang’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 19 ‘湖光山色’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Huguangshanse’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 20 ‘迟白’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Chibai’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 21 ‘雪峰’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Xuefeng’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 22 ‘万寿红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Wanshouhong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 23 ‘粉绫红珠’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Fenlinghongzhu’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 24 ‘竹叶红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Zhuyehong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 25 ‘赵园粉’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Zhaoyuanfen’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 26 ‘紫凤羽’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Zifengyu’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 27 ‘遍地红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Biandihong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 28 ‘墨紫绫’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Moziling’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 29 ‘山河红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Shanhehong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 30 ‘金簪刺玉’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Jinzanciyu’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 31 ‘巧玲’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Qiaoling’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 32 ‘雪盖黄沙’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Xuegaihuangsha’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 33 ‘永生红’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Yongshenghong’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 34 ‘红珠映玉’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Hongzhuyingyu’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 35 ‘鹤落粉池’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Heluofenchi’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 36 ‘火炼赤金’ P.lactiflora Pall.cv.‘Huolianchijin’ 山东菏泽曹州牡丹园 37 芍药 P.lactiflora Pall. 河北张家口市大海陀 Table 1. The experimental materials, Chinese name, scientific name and source
-
Agilent GC-MS7890A气相色谱—质谱联用仪(美国安捷伦公司)、SHB-Ⅲ循环式多用真空泵(郑州长城科工贸易有限公司)、DHG—9240A型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(上海一恒科技有限公司)、BSA2202S分析天平(北京,赛多利斯科学仪器)、XMTD—2MB型恒温水浴锅、索氏提取器等。
-
分析纯无水乙醚、甲醇和氢氧化钾。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 主要仪器
1.3. 主要试剂
-
将芍药种子去除种皮后,放入电热恒温鼓风干燥箱,(75±1)℃的烘箱中干燥24 h,取出后粉碎备用。
-
称取2.50 g芍药籽仁粉末,用定量滤纸包成小包称质量后放入索氏提取器中,萃取溶剂为无水乙醚,料液比1:25;用水浴锅恒温50℃萃取,抽提7 h后,得到淡黄色油脂与乙醚的混合物;放入通风柜中,挥发乙醚,乙醚挥发完全后计算含油率。芍药籽油含油率按下式计算:
式中:X为含油率;M0为芍药籽的质量(g);M1为油脂质量(g)。
-
称取芍药籽油100.0 mg,放入10.0 mL塑料连盖离心管中,加入2.0 mL无水乙醚,充分溶解籽油后,加入0.4 mol·L-1的KOH-甲醇溶液2.0 mL,震荡后放入通风柜,静置45 min后,加入3.0 mL蒸馏水震荡静置30 min,取上层有机相进行分析。
-
色谱柱:AB-FFAP石英毛细管柱,长30 m,内径0.25 mm;载气为氦;柱温从50℃开始,保持1 min,后以15℃·min-1升温至200℃,保持45 min;进样口温度250℃,进样量0.2 μL;检测器温度270℃,柱流速2.19 mL·min-1,柱压20 Psi;恒流模式。
-
通过NIST质谱数据库检索与鉴定色谱图中峰所指示的化学成分[14],采用峰面积归一法自动计算某化学成分的百分比含量,最后用Excel(2003)和SPSS(13.0)软件分析数据。
2.1. 原料预处理
2.2. 索氏提取
2.3. 芍药籽油GC-MS分析
2.3.1. 油脂的甲酯化
2.3.2. GC-MS条件
2.3.3. 分析方法
-
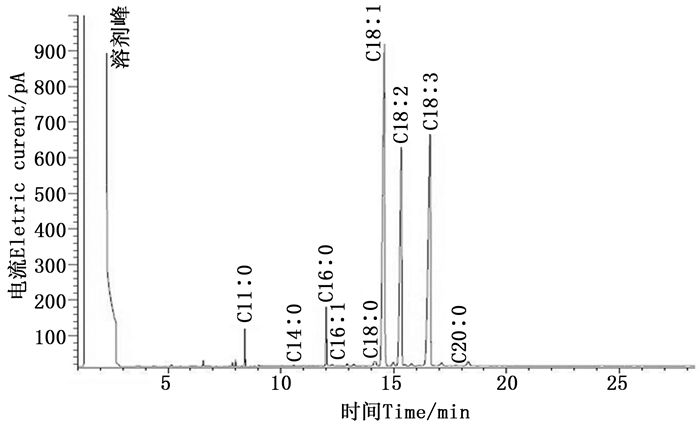
经气相色谱分析检测,从芍药籽油中分离出8种主要脂肪酸成分,分别为豆蔻酸(C14:0)、棕榈酸(C16:0)、棕榈一烯酸(C16:1)、硬脂酸(C18:0)、油酸(C18:1),亚油酸(C18:2),亚麻酸(C18:3)和花生酸(C20:0)(图 1,以32号样品为例),其保留时间依次为10.56、12.10、12.27、14.24、14.57、15.38、16.61、17.98 min,作为标样的十一碳酸甲酯(C11:0)保留时间为8.40 min。不同芍药品种和自然居群种子含油率及脂肪酸成分见表 2。本试验除了检测出8种主要脂肪酸外,还检测出其他多种脂肪酸,由于其含量较小,未对其成分做进一步分析。
% 样品号
Number饱和脂肪酸(SFA) 合计
Total不饱和脂肪酸(UFA) 合计
Total未知脂肪酸
Unknown fatty acid含油率
Oil content豆蔻酸
Myristic acid棕榈酸
Palm acid棕榈一烯酸
Palmtic acid硬脂酸
Stearic acid花生酸
Arachic acid单不饱和脂肪酸
(MUFA)多不饱和脂肪酸
(PUFA)油酸
Oleic acid亚油酸
Linoleic acid亚麻酸
Linolenic acid1 0.04 3.60 0.04 0.01 0.09 3.78 29.91 31.71 33.55 95.17 1.05 18.97 2 0.02 2.49 0.03 0.43 0.12 3.09 32.01 27.20 36.03 95.24 1.67 16.80 3 0.04 3.34 0.05 0.56 0.05 4.04 32.45 21.83 39.75 94.03 1.93 18.00 4 0.02 2.65 0.04 0.02 0.07 2.80 30.88 24.20 40.36 95.44 1.76 20.00 5 0.03 2.78 0.05 0.67 0.06 3.59 30.01 24.93 38.80 93.74 2.67 21.68 6 0.03 2.37 0.13 0.72 0.07 3.32 33.80 26.24 34.09 94.13 2.55 16.02 7 0.02 2.69 0.05 0.78 0.07 3.61 30.30 30.36 32.34 93.00 3.39 21.30 8 0.03 2.81 0.11 0.61 0.06 3.62 31.61 30.31 32.09 94.01 2.37 23.08 9 0.05 3.16 0.07 0.79 0.06 4.13 29.36 26.61 35.55 91.52 4.35 18.80 10 0.03 3.66 0.17 0.84 0.27 4.97 36.15 24.17 27.76 88.08 6.95 17.44 11 0.04 3.58 0.01 0.01 0.01 3.65 32.90 26.66 35.83 95.39 0.96 26.89 12 0.04 3.40 0.04 0.02 0.02 3.52 35.08 28.85 31.33 95.26 1.22 22.96 13 0.03 2.54 0.12 0.70 0.07 3.46 33.08 26.98 34.85 94.91 1.63 15.29 14 0.03 2.56 0.12 0.64 0.02 3.37 32.18 24.66 39.02 95.86 0.77 17.00 15 0.04 2.26 0.16 0.55 0.03 3.04 29.78 24.69 31.80 86.27 10.69 27.24 16 0.05 3.53 0.05 0.01 0.10 3.74 33.51 27.00 34.60 95.11 1.15 25.68 17 0.07 3.32 0.03 1.10 0.05 4.57 36.05 27.62 26.64 90.31 5.12 13.15 18 0.03 3.08 0.05 0.15 0.08 3.39 28.13 29.55 36.68 94.36 2.25 17.97 19 0.03 3.16 0.03 0.63 0.09 3.94 34.41 28.52 32.31 95.24 0.82 21.37 20 0.04 3.35 0.06 0.73 0.07 4.25 31.95 28.89 34.06 94.90 0.85 17.41 21 0.04 2.98 0.10 0.78 0.07 3.97 34.48 30.22 28.61 93.31 2.72 14.00 22 0.02 2.33 0.06 0.68 0.08 3.17 38.05 24.35 33.35 95.75 1.08 18.29 23 0.03 3.16 0.04 0.01 0.02 3.26 38.27 22.83 34.08 95.18 1.56 18.82 24 0.06 3.81 0.07 0.80 0.03 4.77 37.44 17.84 33.19 88.47 6.76 15.09 25 0.04 3.10 0.06 0.67 0.02 3.89 32.48 22.24 38.87 93.59 2.52 27.42 26 0.07 3.84 0.06 0.80 0.06 4.83 37.54 17.90 33.27 88.71 6.46 19.59 27 0.05 2.86 0.09 0.62 0.03 3.65 35.29 24.05 32.03 91.37 4.98 20.51 28 0.04 2.95 0.04 0.44 0.04 3.51 28.29 32.79 33.58 94.66 1.83 20.62 29 0.03 2.88 0.06 0.73 0.03 3.73 30.66 28.79 35.24 94.69 1.58 22.60 30 0.04 2.66 0.06 0.75 0.03 3.54 37.56 23.46 32.68 93.70 2.76 16.73 31 0.04 3.16 0.07 0.77 0.03 4.07 38.60 20.66 33.54 92.80 3.13 19.42 32 0.04 2.66 0.06 0.75 0.03 3.54 37.56 23.46 32.68 93.70 2.76 33.77 33 0.05 3.34 0.09 0.69 0.02 4.19 35.97 23.88 32.90 92.75 3.06 20.27 34 0.04 2.89 0.14 0.79 0.04 3.90 24.68 32.40 35.82 92.90 3.20 16.54 35 0.03 3.07 0.03 0.73 0.03 3.89 32.87 30.21 31.98 95.06 1.05 21.09 36 0.04 3.42 0.14 0.82 0.06 4.48 37.29 22.23 32.53 92.05 3.47 17.25 37 0.05 3.43 0.16 0.38 0.06 4.08 23.80 28.56 41.59 93.95 1.97 28.31 注:饱和脂肪酸含量(SFA)=饱和脂肪酸/总脂肪酸×100%;不饱和脂肪酸含量UFA=不饱和脂肪酸/总脂肪酸×100%。 Table 2. Composition of fatty acids and its relative content of P.lactiflora Pall
从表 2可看出:供试的37份芍药种子的含油率差异显著,平均含油率为20.20%,其中,32号‘雪盖黄沙’的含油率最高(33.77%),比含油率最低的17号‘莲台’(13.15%)高20.62%;含油率超过25%的芍药分别为:32号‘雪盖黄沙’(33.77%)、37号芍药(28.31%)、25号‘赵园粉’(27.42%)、15号‘奇花露霜’(27.24%)、11号‘锦山红’(26.89%)、16号‘蝶落粉池’(25.68%)。不同芍药品种间含油率变异较大,其变异系数为19.47%(表 3),芍药与芍药品种平均含油率相比,变异不大,说明芍药及其品种含油率变化相对稳定,但品种间含油率差异显著,这为选育高含油率芍药品种提供理论依据。
% 项目
Item豆蔻酸
Myristic acid棕榈酸
Palm acid棕榈一烯酸
Palmticacid硬脂酸
Stearic acid油酸
Oleic acid亚油酸
Linoleic acid亚麻酸
Linolenic acid花生酸
Arachic acid含油率
Oil content最大值Maximum 0.07 3.84 0.17 1.10 38.60 32.79 41.59 0.27 33.77 最小值Minimum 0.02 2.26 0.01 0.01 23.80 17.84 26.64 0.01 13.15 平均值Mean 0.04 3.05 0.07 0.57 33.09 26.13 34.15 0.06 20.20 极差Range 0.05 1.58 0.16 1.09 14.80 14.95 14.95 0.26 20.62 标准差Std.deviation 0.01 0.42 0.04 0.29 3.68 3.73 3.27 0.04 4.41 变异系数CV 0.00 0.18 0.002 0.09 13.66 13.90 10.71 0.002 19.47 Table 3. Variation of content of fatty acids in P.lactiflora Pall
-
芍药及其品种间脂肪酸组成成分相同,但相对含量差异显著(表 2、3)。对山东菏泽曹州牡丹园1~36号芍药品种、河北大海陀37号芍药籽油成分和含量分析表明:二者的芍药籽油脂肪酸成分相同,均包含8种主要脂肪酸。1~37号芍药籽油脂肪酸平均相对含量中,亚麻酸含量最高,其次为油酸、亚油酸和棕榈酸,这4种脂肪酸的含量占全部脂肪酸的96.42%,不饱和脂肪酸相对含量达93.37%,硬脂酸、花生酸、棕榈一烯酸、豆蔻酸含量均较小。采自河北大海陀的37号芍药,其籽油的亚麻酸含量在所有供试芍药中含量最高,亚麻酸、亚油酸含量分别比采自菏泽曹州牡丹园1~36号芍药品种平均含量高7.65%、2.50%;山东菏泽曹州牡丹园1~36号油酸平均相对含量为33.35%,比河北大海陀野生芍药高9.55%;棕榈酸、硬脂酸、花生酸等脂肪酸因其本身含量较小,差异不大。
-
利用SPSS13.0对芍药脂肪酸变异情况分析表明:芍药脂肪酸成分中,亚油酸的变异系数最大(13.90%),其次为油酸(13.66%)。不同芍药及品种各脂肪酸成分的变异系数从大到小依次为:亚油酸(13.90%)>油酸(13.66%)>亚麻酸(10.71%)>棕榈酸(0.18%)>硬脂酸(0.09%)>花生酸、棕榈一烯酸(0.002%)>豆蔻酸(0%)。说明芍药亚油酸、亚麻酸、油酸含量高且稳定。
3.1. 不同芍药籽油脂肪酸成分及含油率分析
3.2. 不同芍药籽油脂肪酸含量分析
3.3. 不同芍药籽油脂肪酸变异情况分析
-
芍药种子含油率直接影响芍药能否开发成油料作物。本试验测得芍药种子平均含油率为20.20%,其中,37号芍药种子含油率为28.31%,32号‘雪盖黄沙’含油率达33.77%,单株和平均含油率的检测结果均表明,芍药种子具有较高含油率。本试验测定的37号芍药含油率比李嘉珏[15]介绍的野生芍药种子含油率(25%)高3.31%,比易军鹏等[16]测定的牡丹种子含油率(24.89%)高3.42%,比祖世亨[17]测定的大豆(Glycine max(Linn.)Merr.)种子含油率(21.9%)高6.41%,比刘仁建[18]测定的红花(Carthamus tinctorius L.)种子含油率(19.68%)高8.63%。芍药在草本油料作物中具有较高的含油率优势,具有开发成油料作物的潜力。
本研究测定出芍药共含8种主要脂肪酸,亚麻酸、亚油酸和油酸是芍药籽油最主要的脂肪酸成分,其中,37号芍药籽油不饱和脂肪酸高达93.95%,比已报道的牡丹籽油不饱和脂肪酸含量70.81%[19]、90%[20]、93.23%[21]高23.14%、3.95%、0.72%,特别是亚麻酸含量高达41.59%,比目前市场上主要食用油芝麻油(0.8%)、大豆油(5%~9%)、茶油(1.1%)[22]高几十倍。Ricardo Ayerza(h)[23]研究表明, Salvia hispanica L.籽油的亚麻酸含量随海拔升高而增高,而饱和脂肪酸含量随海拔降低、气温升高而逐渐增高;孟祥勋等[24]对不同海拔高度大豆脂肪酸含量研究也表明,不同海拔高度对各种脂肪酸含量均影响显著,亚油酸和亚麻酸随海拔的增高而增加,棕榈酸和油酸含量随海拔的增加而下降;商志伟等[25]研究表明,在偏高海拔地区种植紫苏(Perilla frutescens (L.)Britt.),其籽粒不饱和脂肪酸含量较高。本试验中,采自河北大海陀的37号芍药籽油中的亚麻酸、亚油酸含量明显高于采自山东菏泽曹州牡丹园的1~36号芍药品种,前者芍药产地的海拔比后者高1 200多m,与以上结论一致,推测其主要原因与芍药产地的海拔和气候条件有关。由于河北张家口市大海陀所产的芍药在菏泽没有种植,关于海拔对芍药种子含油量、脂肪酸成分和含量的关系尚需进一步研究。
-
本文以不同地区不同类型芍药为试验对象,探索了芍药种子含油率、脂肪酸成分及含量,结果表明:芍药种子平均含油率为20.20%,主要含有豆蔻酸、棕榈酸、棕榈一烯酸、硬脂酸、油酸、亚油酸、亚麻酸和花生酸8种脂肪酸,各脂肪酸含量变化相对稳定,其中,亚麻酸、油酸和亚油酸3种不饱和脂肪酸的含量占全部脂肪酸的93.37%,饱和脂肪酸占6.63%。亚麻酸是一种人体自身不能合成却是人体所必需的脂肪酸,因此,开发高亚麻酸含量植物油对于我国食用油的营养价值具有重要意义。本研究证明了芍药种子具有较高含油率,富含亚麻酸、亚油酸和油酸,且含量变化相对稳定,变异很小,具有开发成为高亚麻酸植物油的潜力。





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: