-
花色是观赏植物最重要的观赏性状之一,是植物进化史上最具有适应意义的表型[1]。植物的花色是多种因子协同作用的结果,其中,色素的组成和含量以及不同色素物质的时空组合起着决定性作用[2-4]。花色素类物质主要有类黄酮、类胡萝卜素和花青素等,类胡萝卜素是一类呈黄色、橙色和红色的脂溶性化合物,目前分离和鉴定出的类胡萝卜素多达750余种,是自然界中存在最广的色素[4-8]。
色彩鲜艳的黄色花以其明朗和高贵的感觉而广受喜爱,纯正的黄色花也是石斛兰花色育种的重要目标[8-10]。目前,市场上的黄色石斛兰多为乳白、乳黄和黄绿色,而石斛兰原生种中不乏纯正明黄色种质[9-11],研究黄色花石斛兰原生种花瓣中的类胡萝卜素成分变化,对于明确花色呈色机理及育种具有重要意义。
目前,有关石斛属(Dendrobium Lindl.)花瓣中类胡萝卜素的研究鲜见报道。Kanchit[12]于1984年利用HPLC对部分开黄色花的石斛兰杂交种盛花期花瓣进行了初步研究[12],分析结果表明,类胡萝卜素和叶绿素是使石斛属呈现黄色和绿色的重要色素。Mudalige等[13]调查了石斛兰花瓣中的色素分布,发现黄色花瓣中主要含类胡萝卜素,而其上的红色、深红棕色或褐色印记则是类胡萝卜素和花青素共同作用的结果。关于石斛属类黄酮和花青素合成相关基因的研究已逐渐深入[14],而关于类胡萝卜素合成相关基因的研究还鲜见报道。
鼓槌石斛(Den. chrysotoxum Lindl.)花瓣明黄,唇瓣上常有U型栗色斑块;球花石斛(Den. thyrsiflorum Rchb.f.)和密花石斛(Den. densiflorum Lindl.)唇瓣皆呈金黄色,球花石斛花瓣白色,而密花石斛花瓣淡黄[11];它们均花量大,群体花期长,是著名的春石斛观赏种,也是重要的育种亲本[11]。本研究以鼓槌石斛、密花石斛和球花石斛原生种为材料,定性、定量分析它们盛开期花瓣中的类胡萝卜素,为探讨石斛属黄色花呈色机理和花色育种提供参考。
HTML
-
鼓槌石斛、密花石斛和球花石斛原生种引种自云南,种植于中国林业科学研究院科研温室。选取鼓槌石斛盛开期花瓣、密花石斛和球花石斛盛开期花瓣和唇瓣进行花色描述和类胡萝卜素成分测定。于2017年2—6月取样,选取花蕾均匀、花色一致、生长势一致的6个单株作为6次生物学重复,每个单株随机选取5朵花,将每朵花的花瓣和唇瓣取下,于液氮中快速冷冻后保存于-80℃超低温冰箱备用。每株选取35朵剩余小花进行花色描述。
-
质谱级甲醇购于上海西格玛奥德里奇公司;分析纯乙醇、正己烷购于北京先明乐施公司;质谱级超纯水取自Milli-Q净水器(Millipore,Bedford,MA,USA)。
-
β-胡萝卜素(β-carotene)、叶黄素(Xanthophyll)、番茄红素(Lycopene)和玉米黄素(Zeaxanthin),全部购自于西格玛奥德里奇公司和上海源叶生物科技有限公司,纯度90%及以上。
-
分别选取新鲜的鼓槌石斛盛开期花瓣、密花石斛和球花石斛盛开期花瓣和唇瓣,置于室内光线良好的地方,利用英国皇家园艺学会比色卡(RHSCC)与花瓣和唇瓣的中上部分进行比对,重复15次,选取出现频率最高的结果,对花色进行描述。
-
类胡萝卜素的提取方法在Jumaah等[15]的基础上优化而来。称取30 mg冻干花瓣材料,1 mL丙酮石油醚(1:2)溶液常温避光提取,提取时间为30 min。每个提取进行3次重复。
-
采用Waters公司的合相色谱系统串联三重四极杆质谱仪(ACQUITY UPC2-XEVO-TQ,Waters,USA)进行类胡萝卜素分析,色谱条件为:采用ACQUITY HSS C18 SB(100 mm× 3 mm, 1.8 μm,Waters,USA)色谱柱;检测波长450 nm;流动相组成:A相CO2,B相甲醇;梯度洗脱程序:0~0.5 min,5% B;0.5~5 min,5%至20% B;5~7 min,20% B;7~8 min,20%到5% B;8~10 min,5% B;流速1.5 mL·min-1;柱温40℃;进样量为1 μL;质谱电离源选用电喷雾电离(ESI),在正离子模式下全扫描,扫描范围(m/z)150800 u;毛细管电压:3.0 KV;锥孔电压:40 V;锥形气体流量:50 L·H-1;脱溶剂气流量:600 L·H-1。MassLynxTM(V 4.1,SCN779,Waters,UK)软件用于MS数据采集与处理。
紫外-可见检测波长为450 nm,通过与标准物质的比对,以及紫外-可见吸收光谱保留时间和质谱信息的定性比较,确定类胡萝卜素结构。采用外标法计算各样品中β-胡萝卜素、叶黄素、番茄红素和玉米黄素的含量,重复3次。采用结构相似化合物的外标法确定其它无标准品化合物的含量,重复3次。
1.1. 植物材料
1.1.1. 化学试剂
1.1.2. 标准品
1.2. 试验方法
1.2.1. 花色描述
1.2.2. 类胡萝卜素提取
1.2.3. 类胡萝卜素定性、定量分析
-
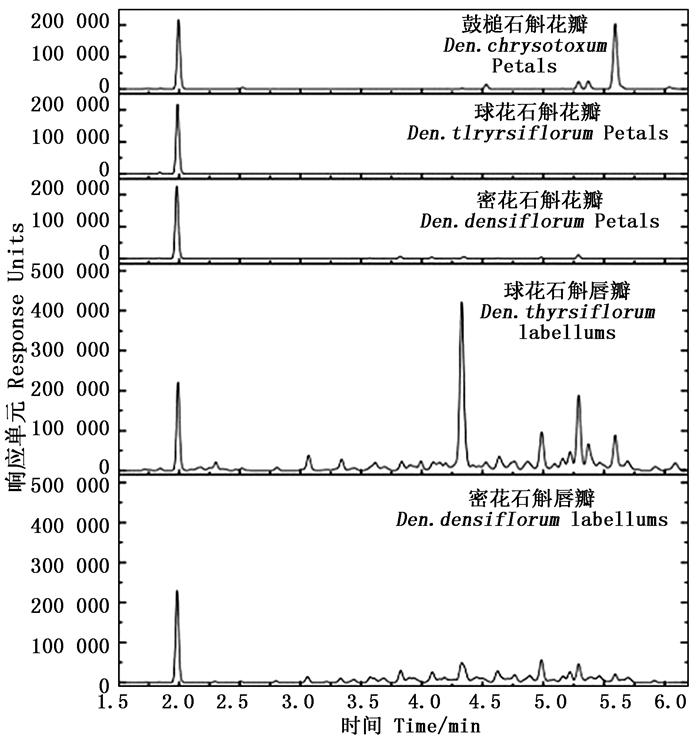
将鼓槌石斛花瓣、密花石斛和球花石斛花瓣和唇瓣与英国皇家园艺比色卡(RHSCC)进行比对,结果(图 1)显示:球花石斛和密花石斛唇瓣皆为金黄色,比色卡代码分别为24A和23A;球花石斛花瓣为白色,比色卡代码为NN155B,基部偶带黄斑;密花石斛花瓣为淡黄色,比色卡代码为11A;鼓槌石斛花瓣为明黄色,比色卡代码为15A。
-
类胡萝卜素分子通常由8个异戊二烯单位连接而成,根据其含氧与否常分为碳水化合物型类胡萝卜素(胡萝卜素)和氧化型类胡萝卜素(叶黄质)。常见的胡萝卜素有α-胡萝卜素、β-胡萝卜素和番茄红素等,极性稍弱。常见的叶黄质有叶黄素、玉米黄质和类胡萝卜素酯等,极性稍强[16]。
通常类胡萝卜素在正离子ESI源模式下电离,产生特征母离子和碎片离子,这些组分在450 nm附近都有强吸收,会产生特征吸收峰[17-18],根据这些吸收峰可以初步推定样品中是否有类胡萝卜素存在。类胡萝卜素分离时,洗脱顺序往往与所测组分的极性密切相关,组分中的羟基数目越多,往往极性越大,如β-胡萝卜素(无-OH)会较早的洗脱,之后是β-隐黄质(1个-OH),随后是玉米黄质(2个-OH)和紫黄质(2个-OH),角黄质(无-OH)也会早于虾青素(2个-OH)洗脱[15]。根据以上推定原则,结合标准品,对3种石斛属植物花瓣和唇瓣中检测到的类胡萝卜素组分进行推定。合相色谱串联三重四极杆质谱仪(UPC2-MS/MS)分析检测到9个类胡萝卜素化合物吸收峰,可以推定的类胡萝卜素化合物结构有8种(表 1),分别是β-胡萝卜素(β-carotene)、α-隐黄质(α-cryptoxanthin)、β-隐黄质(β-cryptoxanthin)、紫黄质(Violaxanthin)、叶黄素(Lutein)、花药黄质(Antheraxanthin)、玉米黄质(Zeaxanthin)和叶黄素酯化物(Lutein-5, 6-epoxide)。
保留时间
Retention time/min检测波长
Detection waudio-video length λmax/nm母离子
Parent ion二级离子(MS2)
Second ion推定结果
Tentative Identification推定依据
Constructive basis2.52 435,461 536 444 β-胡萝卜素β-carotene 标品 4.33 431,458 552 460 α-隐黄素α-cryptoxanthin [15] 4.50 436,462 552 - β-隐黄素β-cryptoxanthin [15] 4.99 431,458 613 335 叶黄素酯化物Lutein-5, 6-epoxide 标品 5.13 429,456 601 - 紫黄质Violaxanthin [15] 5.26 432,459 568 - 叶黄素Lutein 标品 5.33 432,457 584 568 花药黄质Antheraxanthin [15] 5.55 438,463 568 - 玉米黄质Zeaxanthin 标品 注: “-”:未检测到或不存在。Notes: “-”:Not detected or not existed。 Table 1. Analysis of carotenoids in petals and labellums of three species of Dendrobium
-
对推定结构的8种类胡萝卜素进行定量分析,结果(表 2、图 2)表明:球花石斛白色花瓣中的类胡萝卜素总量最低,约为52.26 μg·g-1,随着黄色加深,类胡萝卜素总量逐渐增加,球花石斛金黄色唇瓣中的类胡萝卜素总量最高,达到3 810.89 μg·g-1。
μg·g-1 组分
Component密花石斛-唇瓣
Den. densiflorum labellums密花石斛-花瓣
Den. densiflorum petals球花石斛-唇瓣
Den. thyrsiflorum labellums球花石斛-花瓣
Den. thyrsiflorum petals鼓槌石斛-花瓣
Den. chrysotoxum petalsβ-胡萝卜素β-carotene 14.32±1.38 2.99±0.28 20.06±0.56 0.64±0.05 30.03±2.46 α-隐黄素α-cryptoxanthin 315.61±28.94 29.02±5.35 2 056.96±62.44 - 20.80±1.92 β-隐黄素β-cryptoxanthin 4.18±0.09 - 13.78±1.04 0.05±0.01 23.04±0.51 叶黄素酯化物Lutein-5, 6-epoxide 265.56±24.43 23.30±4.78 431.48±31.12 - 3.89±0.24 紫黄质Violaxanthin 37.17±4.55 2.84±0.46 64.94±0.85 - 10.44±0.08 叶黄素Lutein 247.82±18.34 103.66±10.72 812.20±33.77 51.57±0.72 166.09±3.74 花药黄质Antheraxanthin 41.20±6.21 1.20±0.06 265.57±4.04 - 108.20±4.63 玉米黄质Zeaxanthin 24.36±3.02 - 145.90±3.80 - 451.00±12.41 总计Total 950.22 163.01 3 810.89 52.26 813.49 注:“-”:未检测到或不存在。Notes:“-”:Not detected or not existed. Table 2. Quantitative analysis of carotenoids in petals and labellums of three species of Dendrobium
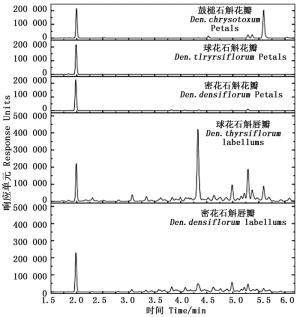
Figure 2. UPC2 chromatograme of carotenoids compounds in petals and labellums of three species of Dendrobium(Detection waudio-videoelength 450 nm)
球花石斛白色花瓣中的类胡萝卜素主要是叶黄素,金黄色唇瓣中α-隐黄素含量最高,约占54%;其次是叶黄素,约占21%,叶黄素酯化物约占11%。密花石斛淡黄色花瓣中叶黄素含量最高,约占64%,其次是α-隐黄素,约占18%,而叶黄素酯化物约占14%;金黄色唇瓣中α-隐黄素含量最高,约占33%,其次是叶黄素酯化物,约占28%,叶黄素约占26%。明黄色鼓槌石斛花瓣中,玉米黄质含量最高,约占55%,其次是叶黄素,约占20%,花药黄质约占13%。
2.1. 花色描述
2.2. 根据UPC2-MS质谱数据对类胡萝卜素化合物推定
2.3. 黄色花石斛兰类胡萝卜素化合物定量分析
-
类胡萝卜素分子由中央多聚共轭双烯链和位于两端的末端基团组成,类胡萝卜素的共轭双链不稳定,易降解,加热和光照都会加速它的异构化,同时天然类胡萝卜素异构体极为复杂,一个双键位置的移动,便会形成α-胡萝卜素/β-胡萝卜素或叶黄素/玉米黄质的切换。给分离、纯化与分析带来了极大的困难[16]。
蔬菜、水果中的类胡萝卜素多以脂肪酸酯的形式存在,提取时常通过皂化处理水解类胡萝卜素酯,释放其包含的色素,同时避免叶绿素干扰,但皂化常使类胡萝卜素总量减少[19-21]。花瓣中的类胡萝卜素多以含氧叶黄素的形式存在,提取时的皂化处理常造成类胡萝卜素水解,从而使分离到的类胡萝卜素组分和总量减少[22]。
测定类胡萝卜素常用方法有薄层色谱法(TLC)、开放柱色谱法(OCC)、逆流液相色谱法(CCC)、高效液相色谱法(HPLC)、超高效液相色谱法(UPLC)和超临界流液体色谱(SFC)[15]。HPLC是目前国内外应用比较普遍的类胡萝卜素分析方法,运用反相性强的C30柱可以测定出样品中痕量的类胡萝卜素,但分析时间长且一些异构体分离困难[15]。SFC也常用于分离类胡萝卜素,其流动相以CO2为主,对极性低的脂溶性物质有极强溶解力,可以有效地分离样品中的类胡萝卜素组分,同时采用的温和分析温度可避免类胡萝卜素受热分解[15]。超高效合相色谱(UPC2)结合了UPLC和SFC技术优点,该方法以超临界CO2为主要的流动相,具有溶剂用量省,分析时间短,分离效率高及检测灵敏度高等优点,将分析物在色谱柱上发生降解的风险降到最低,可以有效地分离类胡萝卜素的同分异构体[15]。
-
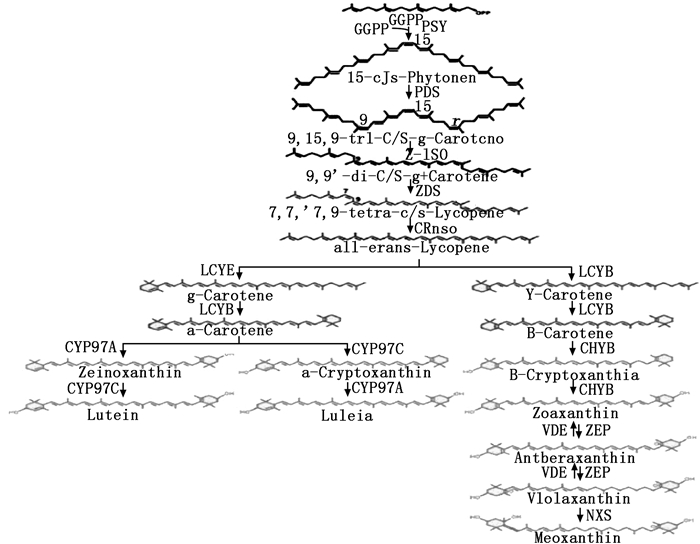
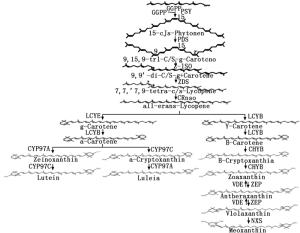
目前,有关植物类胡萝卜素的主要代谢途径、代谢中间产物及参与合成的关键酶和基因已基本明确(图 3)[5-8],类胡萝卜素生物合成起始于两分子的GGPP,在八氢番茄红素合成酶(PSY)的作用下缩合形成无色八氢番茄红素,随后经八氢番茄红素脱氢酶(PDS)、ξ-胡萝卜素异构酶(Z-ISO)、ξ-胡萝卜素脱氢酶(ZDS)和胡萝卜素异构酶(CRTISO)的共同作用形成全反式番茄红素[5-8]。之后的番茄红素环化是类胡萝卜素代谢中的重要分支点,植物中存在2种番茄红素环化酶LCYB和LCYE,可分别催化番茄红素的一端生成β环和γ环[5-8]。LCYB和LCYE催化番茄红素形成一端β环一端γ环的α-胡萝卜素衍生物;而经LCYB的2次催化,番茄红素形成两端为β环的β-胡萝卜素衍生物[5-8]。α-胡萝卜素在非血红素铁加氧酶类氢化酶(CYP97A)和细胞色素P450加氧酶(CYP97C)的共同作用下合成叶黄素。β-胡萝卜素在β-胡萝卜素氢化酶(CHYB)、玉米黄素环氧酶(ZEP)和新黄质合成酶(NSY)的作用下形成新黄质[6-8]。
不同花色间的类胡萝卜素积累具有特异性,本研究发现,白色球花石斛花瓣中类胡萝卜素含量极少,淡黄色密花石斛花瓣中以α-胡萝卜素衍生物叶黄素为主,约占类胡萝卜素总量的90%以上,这与Kanchit[12]淡黄色石斛花中叶黄素极高的研究结果相似。金黄色球花石斛和密花石斛唇瓣中的α-胡萝卜素衍生物如α-隐黄素和叶黄素含量极高,约占类胡萝卜素总量的85%以上,这与金盏菊(Calendula officinalis Hohen.)[23]、万寿菊(Tagetes erecta Linn.)[24]和宫灯百合(Sandersonia aurantiaca Hook.)[25]的研究结果相一致,在它们的花瓣中叶黄素及叶黄素衍生物达到花瓣总类胡萝卜素含量的90%以上。明黄色花瓣(鼓槌石斛花瓣)中β-胡萝卜素衍生物玉米黄质和花药黄质含量较高,约占69%,同样的研究结果也出现在杂交文心兰(Oncidium hybridum)明黄色唇瓣中,β-胡萝卜素衍生物的含量较高[26]。在Kanchit[12]的研究结果中也有类似发现,亮黄色及橙黄色石斛兰杂交种的花瓣中β-胡萝卜素衍生物如玉米黄质、花药黄质和新黄质含量较高[12]。
-
目前,黄色花石斛兰的育种主要依赖于传统的杂交育种,以尖刀唇石斛(Den. heterocarpum)及黄喉石斛(Den. signatum)为黄花育种基础,配合金钗石斛(Den. nobile)杂交出Den. Thwaitesiae等近乎黄色的品种[10]。在黄色花春石斛育种中,子代常常呈现不黄不白或初开时偏黄,越开越白的“褪色”现象[10],可能与父母本中含有具强势遗传特性的白花血统有关[10]。随着花色分子生物学研究的深入,分子育种已成为改良植物花色的重要途径,目前,有关植物类胡萝卜素合成相关途径的关键基因也已被分离鉴定[5-8, 27],这为通过导入外源基因或阻断其相关代谢途径来进行花色遗传性状改良提供了极大可能。结合本研究对黄色花石斛兰盛开期花瓣中类胡萝卜素种类和含量的分析结果,推测浅黄色和金黄色石斛花瓣中类胡萝卜素代谢途径以α-胡萝卜素合成支路为主,而明黄色石斛花瓣中类胡萝卜素代谢途径以β-胡萝卜素合成支路为主。在番茄红素环化的过程中,LCYE的表达水平一定程度上会决定β-和α-两个分支间的类胡萝卜素比例[27-28]。推测在黄色花石斛兰中通过调控LCYE基因的表达,有可能实现石斛的花色品质定向遗传改良,将对石斛兰黄色花育种具有重要意义。
3.1. 类胡萝卜素测定方法
3.2. 黄色花石斛兰的类胡萝卜素积累
3.3. 黄色花石斛兰育种
-
以花色为黄色的鼓槌石斛、密花石斛和球花石斛的盛开期花瓣和唇瓣为试验材料,进行类胡萝卜素的定性、定量分析。结果表明:3种石斛属植物花瓣和唇瓣的色系可分为白色系和浅黄-明黄-金黄色系,在黄色花石斛兰中共鉴定出8种类胡萝卜素组分,分别是β-胡萝卜素、α-隐黄质、β-隐黄质、紫黄质、叶黄素、花药黄质、玉米黄质和叶黄素酯化物。定量分析显示:球花石斛白色花瓣中类胡萝卜素的含量极少,随着黄色加深,类胡萝卜素总量逐渐增加,球花石斛金黄色唇瓣中的类胡萝卜素总量达到最高。密花石斛淡黄色花瓣以叶黄素为主;球花石斛和密花石斛金黄色唇瓣中主要为α-隐黄素、叶黄素和叶黄素酯化物;明黄色鼓槌石斛花瓣中以玉米黄质、花药黄质和叶黄素为主。根据前人研究的类胡萝卜素合成途径及黄色花石斛兰中的类胡萝卜素检测结果,推测淡黄色和金黄色石斛花瓣中类胡萝卜素主要是α-胡萝卜素及其衍生物,而明黄色石斛花瓣中类胡萝卜素主要是β-胡萝卜素及其衍生物。推测通过调控LCYE基因的表达,可能实现黄色花石斛的花色定向改良。






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: